The Innovative Medicines Initiative neurodegeneration portfolio: From individual projects to collaborative networks
- PMID: 36408524
- PMCID: PMC9666729
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.994301
The Innovative Medicines Initiative neurodegeneration portfolio: From individual projects to collaborative networks
Abstract
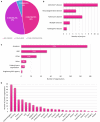
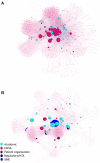
The IMI public-private partnership between the European Commission and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) was launched in 2008 with an initial budget of €2 billion. Aiming to accelerate the development of innovative medicines for areas of unmet clinical need, the IMI has committed over €380 million to projects on neurodegenerative disorders (NDD), catalyzing public-private collaborations at scale and at all stages of the R&D pipeline. Because of this vast investment, research on neurodegenerative diseases has made enormous strides in recent decades. The challenge for the future however remains to utilize this newly found knowledge and generated assets to develop better tools and novel therapeutic strategies. Here, we report the results of an integrated programme analysis of the IMI NDD portfolio, performed by the Neuronet Coordination and Support Action. Neuronet was launched by the IMI in 2019 to boost synergies and collaboration between projects in the IMI NDD portfolio, to increase the impact and visibility of research, and to facilitate interactions with related initiatives worldwide. Our analysis assessed the characteristics, structure and assets of the project portfolio and identifies lessons from projects spanning preclinical research to applied clinical studies and beyond. Evaluation of project parameters and network analyses of project partners revealed a complex web of 236 partnering organizations, with EFPIA partners often acting as connecting nodes across projects, and with a great diversity of academic institutions. Organizations in the UK, Germany, France and the Netherlands were highly represented in the portfolio, which has a strong focus on clinical research in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease in particular. Based on surveys and unstructured interviews with NDD research leaders, we identified actions to enhance collaboration between project partners, by improving the structure and definition of in-kind contributions; reducing administrative burdens; and enhancing the exploitation of outcomes from research investments by EU taxpayers and EFPIA. These recommendations could help increase the efficiency and impact of future public-private partnerships on neurodegeneration.
Keywords: IMI; collaboration; neurodegeneration; public-private partnership; research policy.
Copyright © 2022 O'Rourke, Coll-Padrós, Bradshaw, Killin, Pradier, Georges, Dawoud, Steukers and Diaz.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors NC-P, LK, and CD were employed by SYNAPSE Research Management Partners. Author LP was employed by Sanofi. Author LS was employed by Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Participating in innovative medicines initiative funded neurodegenerative disorder projects-An impact analysis conducted as part of the NEURONET project.Front Neurol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1140722. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1140722. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37006486 Free PMC article.
-
The innovative medicines initiative: a European response to the innovation challenge.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Mar;91(3):418-25. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2011.321. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22318619 Review.
-
The innovative medicines initiative: a public private partnership model to foster drug discovery.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2013 Nov 27;6:e201303017. doi: 10.5936/csbj.201303017. eCollection 2013. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2013. PMID: 24688725 Free PMC article.
-
Public-private partnership models in France and in Europe.Therapie. 2006 Jul-Aug;61(4):325-34, 313-23. doi: 10.2515/therapie:2006059. Therapie. 2006. PMID: 17124948 Review. English, French.
-
The European Prevention of Alzheimer's Dementia Programme: An Innovative Medicines Initiative-funded partnership to facilitate secondary prevention of Alzheimer's disease dementia.Front Neurol. 2022 Nov 22;13:1051543. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1051543. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36484017 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Participating in innovative medicines initiative funded neurodegenerative disorder projects-An impact analysis conducted as part of the NEURONET project.Front Neurol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1140722. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1140722. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37006486 Free PMC article.
-
Data sharing in neurodegenerative disease research: challenges and learnings from the innovative medicines initiative public-private partnership model.Front Neurol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1187095. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1187095. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37545729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of experimental medicine approaches for the development of novel psychiatric treatments based on orexin receptor modulation.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023 Apr;147:105107. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105107. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023. PMID: 36828161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Socio-Economic Impact Report on IMI1 projects . London. Available online at: https://www.imi.europa.eu/sites/default/files/uploads/documents/referenc... (accessed March 1, 2021).
-
- IMI Innovative Medicines Initiative . Strategic Research Agenda. Available online at: https://www.imi.europa.eu/about-imi/strategic-research-agenda (accessed March 1, 2021).
-
- RStudio Team (2018). RStudio: Integrated Development for R. Boston, MA: RStudio, PBC. Available online at: http://www.rstudio.com/
-
- Csardi G, Nepusz T. The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJ. (2006) 1695. Available online at: https://igraph.org (accessed April 6, 2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

