One- and Two-Dose Vaccinations With Modified Vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic Induce Durable B-Cell Memory Responses Comparable to Replicating Smallpox Vaccines
- PMID: 36408618
- PMCID: PMC10175071
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiac455
One- and Two-Dose Vaccinations With Modified Vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic Induce Durable B-Cell Memory Responses Comparable to Replicating Smallpox Vaccines
Abstract
Background: Although modified vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) vaccination is approved for smallpox and monkeypox prevention, immunological persistence and booster effects remain undescribed.
Methods: Participants naive to smallpox vaccination were randomized to 1 dose MVA-BN (1×MVA, n = 181), 2 doses MVA-BN (2×MVA, n = 183), or placebo (n = 181). Participants with previous smallpox vaccination received 1 MVA-BN booster (HSPX, n = 200). Subsets of the formerly naive groups (approximately 75 each) received an MVA-BN booster 2 years later.
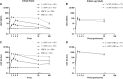
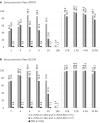
Results: Neutralizing antibody (nAb) geometric mean titers (GMTs) increased from 1.1 (baseline, both naive groups) to 7.2 and 7.5 (week 4, 1×MVA and 2×MVA, respectively), and further to 45.6 (week 6, 2×MVA after second vaccination). In HSPX, nAb GMT rapidly increased from 21.6 (baseline) to 175.1 (week 2). At 2 years, GMTs for 1×MVA, 2×MVA, and HSPX were 1.1, 1.3, and 10.3, respectively. After boosting in the previously naive groups, nAb GMTs increased rapidly in 2 weeks to 80.7 (1×MVA) and 125.3 (2×MVA), higher than after primary vaccination and comparable to boosted HSPX subjects. Six months after boosting, GMTs were 25.6 (1×MVA) and 49.3 (2×MVA). No safety concerns were identified.
Conclusions: Anamnestic responses to boosting without sustained high nAb titers support presence of durable immunological memory following primary MVA-BN immunization. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT00316524 and NCT00686582.
Keywords: booster; memory response; monkeypox; orthopoxvirus; recall response; revaccination; vaccinia experienced.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. H.I. is a former employee of Harrison Clinical Research Deutschland GmbH; N. S., D. R., D. S., J. D. P., T. P. H. M., G. S., R. N., H. W., and L. C. are current or former employees and stakeholders of Bavarian Nordic; L. d. M. is the company CMO and P. C. is the company CEO. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Fine PE, Jezek Z, Grab B, Dixon H. The transmission potential of monkeypox virus in human populations. Int J Epidemiol 1988; 17:643–50. - PubMed
-
- Petersen BW, Harms TJ, Reynolds MG, Harrison LH. Use of vaccinia virus smallpox vaccine in laboratory and health care personnel at risk for occupational exposure to orthopoxviruses—recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016; 65:257–62. - PubMed
-
- Jezek Z, Gromyko AI, Szczeniowski MV. Human monkeypox. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol 1983; 27:13–28. - PubMed

