Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-aminoquinoline derivatives as receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 (RIPK2) inhibitors
- PMID: 36408835
- PMCID: PMC9683047
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2148317
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-aminoquinoline derivatives as receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 (RIPK2) inhibitors
Abstract
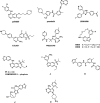
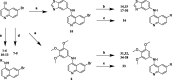
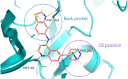
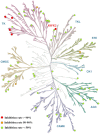
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 (RIPK2) is an essential protein kinase mediating signal transduction by NOD1 and NOD2, which play an important role in regulating immune signalling. In this study, we designed and synthesised a novel series of 4-aminoquinoline-based derivatives as RIPK2 inhibitors. In vitro, compound 14 exhibited high affinity (IC50 = 5.1 ± 1.6 nM) and excellent selectivity to RIPK2 showing in a dendrogram view of the human kinome phylogenetic tree. Bearing favourable lipophilicity and eligible lipophilic ligand efficiency (LipE), compound 14 was selected to investigate cellular anti-inflammatory effect and was identified as a potent inhibitor to reduce the secretion of MDP-induced TNF-α with a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, compound 14 showed moderate stability in human liver microsome. Given these promising results, compound 14 could serve as a favourable inhibitor of RIPK2 for further physiological and biochemical research so as to be used in therapeutic treatment.
Keywords: NOD; RIPK2 inhibitor; immunity; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
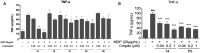
Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel thieno[2,3d]pyrimidine derivatives as potent and specific RIPK2 inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2024 Jan 1;97:129567. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129567. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 38008339
-
Discovery of Potent and Selective Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase 2 (RIPK2) Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs).J Med Chem. 2022 Jul 14;65(13):9312-9327. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00604. Epub 2022 Jun 16. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35709396
-
4-Anilinoquinazoline Derivatives as the First Potent NOD1-RIPK2 Signaling Pathway Inhibitors at the Nanomolar Range.J Med Chem. 2024 Nov 14;67(21):19304-19322. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01713. Epub 2024 Oct 23. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39444201
-
RIPK2 NODs to XIAP and IBD.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan;109:144-150. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 32631784 Review.
-
RIPK2 as a promising druggable target for autoimmune diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 May;118:110128. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110128. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37023697 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis, and antiproliferative screening of new quinoline derivatives bearing a cis-vinyl triamide motif as apoptosis activators and EGFR-TK inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2024 Aug 7;14(34):24781-24790. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04915b. eCollection 2024 Aug 5. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39114435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chamaillard M, Hashimoto M, Horie Y, et al. . An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat Immunol. 2003;4(7):702–707. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
