CHD6 promotes broad nucleosome eviction for transcriptional activation in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 36408932
- PMCID: PMC9757051
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac1090
CHD6 promotes broad nucleosome eviction for transcriptional activation in prostate cancer cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to 'CHD6 promotes broad nucleosome eviction for transcriptional activation in prostate cancer cells'.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Mar 21;51(5):2498. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad114. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36794715 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
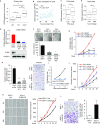
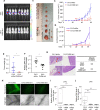
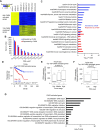
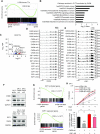
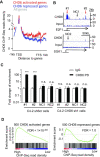
Despite being a member of the chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein family, little is known about the exact role of CHD6 in chromatin remodeling or cancer disease. Here we show that CHD6 binds to chromatin to promote broad nucleosome eviction for transcriptional activation of many cancer pathways. By integrating multiple patient cohorts for bioinformatics analysis of over a thousand prostate cancer datasets, we found CHD6 expression elevated in prostate cancer and associated with poor prognosis. Further comprehensive experiments demonstrated that CHD6 regulates oncogenicity of prostate cancer cells and tumor development in a murine xenograft model. ChIP-Seq for CHD6, along with MNase-Seq and RNA-Seq, revealed that CHD6 binds on chromatin to evict nucleosomes from promoters and gene bodies for transcriptional activation of oncogenic pathways. These results demonstrated a key function of CHD6 in evicting nucleosomes from chromatin for transcriptional activation of prostate cancer pathways.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Natesan R., Aras S., Effron S.S., Asangani I.A.. Epigenetic regulation of chromatin in prostate cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019; 1210:379–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

