Similar and Divergent Roles of Stringent Regulator (p)ppGpp and DksA on Pleiotropic Phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 36409141
- PMCID: PMC9769547
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02055-22
Similar and Divergent Roles of Stringent Regulator (p)ppGpp and DksA on Pleiotropic Phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
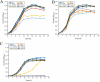
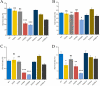
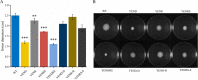
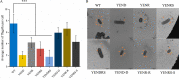
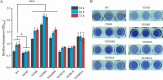
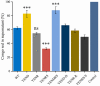
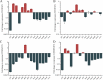
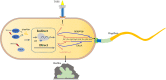
Stringent response plays an important role in the response of Enterobacteriaceae pathogens to rapid environmental changes. It has been shown that synergistic and antagonistic actions exist between the signaling molecules (p)ppGpp and DksA in several foodborne pathogens; however, the biological function of these molecules and their interactions in Yersinia are still unclear. This study systematically investigated the role of stringent response in Yersinia enterocolitica, a typical foodborne Enterobacteriaceae pathogen, by deleting the (p)ppGpp and DksA biosynthesis genes. (p)ppGpp and DksA copositively regulated most phenotypes, such as motility, antibiotic resistance, and tolerance to oxidative stress, whereas they exhibited independent and/or divergent roles in the growth and biofilm synthesis of Y. enterocolitica. Gene expression analysis revealed that (p)ppGpp- and DksA-deficiency reduced the transcription of flagellar synthesis genes (fliC and flgD) and biofilm synthesis genes (bssS and hmsHFRS), which could potentially contribute to changes in motility and biofilm formation. These results indicate that stringent response regulators (p)ppGpp and DksA have a synergistic role and independent or even completely opposite biological functions in regulating genes and phenotypes of Y. enterocolitica. Our findings revealed the biofunctional relationships between (p)ppGpp and DksA and the underlying molecular mechanisms in the regulation of the pathogenic phenotype of Y. enterocolitica. IMPORTANCE The synergetic actions between the stringent response signaling molecules, (p)ppGpp and DksA, have been widely reported. However, recent transcriptomic and phenotypic studies have suggested that independent or even opposite actions exist between them. In this study, we demonstrated that the knockout of (p)ppGpp and DksA affects the polymorphic phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Although most of the tested phenotypes, such as motility, antibiotic resistance, and tolerance to oxidative stress, were copositively regulated by (p)ppGpp and DksA, it also showed inconsistencies in biofilm formation ability as well as some independent phenotypes. This study deepens our understanding of the strategies of foodborne pathogens to survive in complex environments, so as to provide theoretical basis for the control and treatment of these microorganisms.
Keywords: (p)ppGpp; DksA; Yersinia enterocolitica; stress resistance; stringent response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dalebroux ZD, Swanson MS. 2012. ppGpp: magic beyond RNA polymerase. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:203–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

