Gender differences in Alzheimer's may be associated with TLR4-LYN expression in damage associated microglia and neuronal phagocytosis
- PMID: 36409648
- PMCID: PMC10199960
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.30916
Gender differences in Alzheimer's may be associated with TLR4-LYN expression in damage associated microglia and neuronal phagocytosis
Abstract
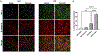
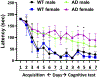
The role of Aβ plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis have recently come into question due to failure of many pharmaceutical agents targeting these deposits and detection of these misfolded proteins in normal human brains. Therefore, we investigated correlations between microglial activation and toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) and Lck/Yes novel tyrosine (LYN) kinase signaling in an AD mouse model. In this study, we used 5-6-month-old 5XFAD and wild type (WT) male and female mice. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and flow cytometry (FC) were performed on their brains. Cognitive performance was assessed with the Barnes-Maze. IHC showed more Ab aggregation in microglia of female 5XFAD mice compared to their male counterparts. Increased co-localization of microglial TLR4 and LYN was also observed in AD more than WT and females more than males. IHC also suggests microglial phagocytosis of neurons in AD mice, which is supported by FC data. Our FC data also support the involvement of disease associated microglia (DAMs) in this process based on cytokine secretion. Cognitive assessment by the Barnes maze showed 5XFAD females performed worse than males. In this study, we investigated the relationship between microglial TLR4 and LYN kinase in 5XFAD male and females. Our data reveals a correlation between microglial TLR4 and LYN co-localization and AD pathogenesis, more in females than males. Targeting microglial TLR4 and Lyn in DAMs may offer new therapeutic opportunities in the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's; LYN‐kinase; cognitive dysfunction; disease associated microglia; phagocytosis; toll like receptor‐4.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


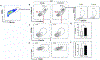


Similar articles
-
Microglial TLR4-Lyn kinase is a critical regulator of neuroinflammation, Aβ phagocytosis, neuronal damage, and cell survival in Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 3;15(1):11368. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96456-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40175501 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 mutation reduces microglial activation, increases Aβ deposits and exacerbates cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Aug 9;8:92. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-92. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21827663 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial pathogens induce neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease mice: protection by microglial regulation.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jan 6;19(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02369-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 34991645 Free PMC article.
-
An overview on microglial origin, distribution, and phenotype in Alzheimer's disease.J Cell Physiol. 2024 Jun;239(6):e30829. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30829. Epub 2022 Jul 13. J Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 35822939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR4 Cross-Talk With NLRP3 Inflammasome and Complement Signaling Pathways in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 23;11:724. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00724. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32391019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex Dependent Disparities in the Central Innate Immune Response after Moderate Spinal Cord Contusion in Rat.Cells. 2024 Apr 6;13(7):645. doi: 10.3390/cells13070645. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607084 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Sexual Dimorphism of Brain Cells during Aging.Brain Sci. 2023 Jan 24;13(2):195. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13020195. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 36831738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promotion of neuroinflammation in select hippocampal regions in a mouse model of perimenopausal Alzheimer's disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 14;12:1597130. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1597130. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40438709 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a 3D Brain Model to Study Sex-Specific Neuroinflammation After Hemorrhagic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Jun;16(3):655-671. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01243-y. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 38558012 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial TLR4-Lyn kinase is a critical regulator of neuroinflammation, Aβ phagocytosis, neuronal damage, and cell survival in Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 3;15(1):11368. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96456-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40175501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balducci C, Frasca A, Zotti M, La Vitola P, Mhillaj E, Grigoli E, … Forloni G (2017). Toll-like receptor 4-dependent glial cell activation mediates the impairment in memory establishment induced by beta-amyloid oligomers in an acute mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav Immun, 60, 188–197. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2016.10.012 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

