Altered serum adiponectin and interleukin-8 levels are associated in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder: A case-control study
- PMID: 36409748
- PMCID: PMC9678262
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276619
Altered serum adiponectin and interleukin-8 levels are associated in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder: A case-control study
Abstract
Background: Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a complex mental health condition that results in several obstacles including disabilities, loss of productivity, and economic burdens on both patients and society. Etiopathogenesis of MDD involves several factors such as sociodemographic, genetic, and biological determinants. However, any suitable biomarkers for risk assessment of depression have not been established yet. Alterations of cytokine are assumed to be involved in the pathophysiology and severity of the depressive disorder. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate serum adiponectin and interleukin-8 (IL-8) among MDD patients in Bangladesh.
Methods: We recruited a total of 63 MDD patients and 94 age-sex matched healthy controls (HCs) in the present study. MDD patients were enrolled from a tertiary care teaching hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh, and HCs from surrounding parts of Dhaka city. A psychiatrist assessed all the study participants following the criteria mentioned in the DSM-5. We applied the Hamilton depression (Ham-D) rating scale to assess the depression severity. Serum adiponectin and IL-8 levels were determined using ELISA kits (BosterBio, USA).
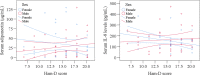
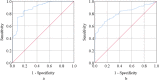
Results: The mean serum concentration of adiponectin was decreased (30.67±4.43 μg/mL vs. 53.81±5.37 μg/mL), and the IL-8 level was increased (160.93±14.84 pg/mL vs. 88.68±6.33 pg/mL) in MDD patients compared to HCs. Sex-specific scatters plot graphs showed the distribution of adiponectin and IL-8 levels with Ham-D scores in MDD patients. Also, ROC curve analysis demonstrated good predictive performances of serum adiponectin and IL-8 for MDD with the area under the curve (AUC) as 0.895 and 0.806, respectively.
Conclusion: The present study findings suggest that alterations of serum adiponectin and IL-8 levels in MDD patients might be involved in the disease process. Therefore, we can use these changes of cytokines in serum levels as early risk assessment tools for depression. The present study findings should be considered preliminary. We propose further interventional studies to evaluate the exact role of adiponectin and IL-8 in depression.
Copyright: © 2022 Islam et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

