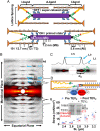
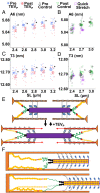
Titin force in muscle cells alters lattice order, thick and thin filament protein formation
- PMID: 36409887
- PMCID: PMC9860331
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2209441119
Titin force in muscle cells alters lattice order, thick and thin filament protein formation
Abstract
Skeletal muscle force production is increased at longer compared to shorter muscle lengths because of length-dependent priming of thick filament proteins in the contractile unit before contraction. Using small-angle X-ray diffraction in combination with a mouse model that specifically cleaves the stretch-sensitive titin protein, we found that titin cleavage diminished the length-dependent priming of the thick filament. Strikingly, a titin-sensitive, length-dependent priming was also present in thin filaments, which seems only possible via bridge proteins between thick and thin filaments in resting muscle, potentially myosin-binding protein C. We further show that these bridges can be forcibly ruptured via high-speed stretches. Our results advance a paradigm shift to the fundamental regulation of length-dependent priming, with titin as the key driver.
Keywords: X-ray diffraction; elasticity; length-dependent activation; mouse; ultrastructure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M., Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature 233, 533–538 (1971). - PubMed
-
- Martyn D. A., Gordon A. M., Length and myofilament spacing-dependent changes in calcium sensitivity of skeletal fibres: Effects of pH and ionic strength. J. Muscle. Res. Cell Motil. 9, 428–445 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

