Synthetic engineering and biological containment of bacteriophages
- PMID: 36409909
- PMCID: PMC9860248
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2206739119
Synthetic engineering and biological containment of bacteriophages
Abstract
The serious threats posed by drug-resistant bacterial infections and recent developments in synthetic biology have fueled a growing interest in genetically engineered phages with therapeutic potential. To date, many investigations on engineered phages have been limited to proof of concept or fundamental studies using phages with relatively small genomes or commercially available "phage display kits". Moreover, safeguards supporting efficient translation for practical use have not been implemented. Here, we developed a cell-free phage engineering and rebooting platform. We successfully assembled natural, designer, and chemically synthesized genomes and rebooted functional phages infecting gram-negative bacteria and acid-fast mycobacteria. Furthermore, we demonstrated the creation of biologically contained phages for the treatment of bacterial infections. These synthetic biocontained phages exhibited similar properties to those of a parent phage against lethal sepsis in vivo. This efficient, flexible, and rational approach will serve to accelerate phage biology studies and can be used for many practical applications, including phage therapy.
Keywords: bacteriophage; biological containment; cell-free genome engineering; phage therapy; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
S.M. and H.A. filed a patent application. Other authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
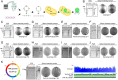
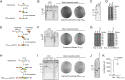
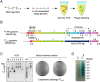
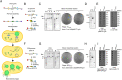
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

