Poly(aspartic acid)-Based Polymeric Nanoparticle for Local and Systemic mRNA Delivery
- PMID: 36409995
- PMCID: PMC9826779
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00738
Poly(aspartic acid)-Based Polymeric Nanoparticle for Local and Systemic mRNA Delivery
Abstract
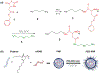
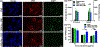
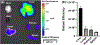
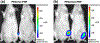
Recently, therapeutics based on mRNA (mRNA) have attracted significant interest for vaccines, cancer immunotherapy, and gene editing. However, the lack of biocompatible vehicles capable of delivering mRNA to the target tissue and efficiently expressing the encoded proteins impedes the development of mRNA-based therapies for a variety of diseases. Herein, we report mRNA-loaded polymeric nanoparticles based on diethylenetriamine-substituted poly(aspartic acid) that induce protein expression in the lungs and muscles following intravenous and intramuscular injections, respectively. Animal studies revealed that the amount of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the nanoparticle surface affects the translation of the delivered mRNA into the encoded protein in the target tissue. After systemic administration, only mRNA-loaded nanoparticles modified with PEG at a molar ratio of 1:1 (PEG/polymer) induce protein expression in the lungs. In contrast, protein expression was detected only following intramuscular injection of mRNA-loaded nanoparticles with a PEG/polymer ratio of 10:1. These findings suggest that the PEG density on the surface of poly(aspartic acid)-based nanoparticles should be optimized for different delivery routes depending on the purpose of the mRNA treatment.
Keywords: PEGylation; gene therapy; mRNA delivery; polymeric nanoparticle; systemic delivery.
Figures
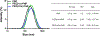
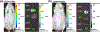
Similar articles
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
-
A poly(amidoamine)-based polymeric nanoparticle platform for efficient in vivo delivery of mRNA.Biomater Adv. 2024 Jan;156:213713. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213713. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Biomater Adv. 2024. PMID: 38071770
-
Optimization of a Degradable Polymer-Lipid Nanoparticle for Potent Systemic Delivery of mRNA to the Lung Endothelium and Immune Cells.Nano Lett. 2018 Oct 10;18(10):6449-6454. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02917. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Nano Lett. 2018. PMID: 30211557 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer-Lipid Nanoparticles for Systemic Delivery of mRNA to the Lungs.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016 Oct 24;55(44):13808-13812. doi: 10.1002/anie.201608450. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016. PMID: 27690187 Free PMC article.
-
Pegylated poly(lactide) and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: preparation, properties and possible applications in drug delivery.Curr Drug Deliv. 2004 Oct;1(4):321-33. doi: 10.2174/1567201043334605. Curr Drug Deliv. 2004. PMID: 16305394 Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA nanodelivery systems: targeting strategies and administration routes.Biomater Res. 2023 Sep 22;27(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40824-023-00425-3. Biomater Res. 2023. PMID: 37740246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannose/stearyl chloride doubly functionalized polyethylenimine as a nucleic acid vaccine carrier to promote macrophage uptake.Drug Deliv. 2024 Dec;31(1):2427138. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2024.2427138. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39540234 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-like structures for combination antigen protein mRNA vaccination.Nat Nanotechnol. 2024 Aug;19(8):1224-1233. doi: 10.1038/s41565-024-01679-1. Epub 2024 May 27. Nat Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38802667 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled Release of Poly(U) via Acetalated Dextran Microparticles for Enhanced Vaccine Adjuvant Delivery.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 21:2025.07.16.665134. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.16.665134. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40777285 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
mRNA Delivery: Challenges and Advances through Polymeric Soft Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):1739. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031739. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barbier AJ; Jiang AY; Zhang P; Wooster R; Anderson DG, The clinical progress of mRNA vaccines and immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol 2022, 40, 840–854. - PubMed
-
- Ibba ML; Ciccone G; Esposito CL; Catuogno S; Giangrande PH, Advances in mRNA non-viral delivery approaches. Adv. Drug Del. Rev 2021, 177, 113930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

