Topography-mediated immunomodulation in osseointegration; Ally or Enemy
- PMID: 36410109
- PMCID: PMC10148651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121903
Topography-mediated immunomodulation in osseointegration; Ally or Enemy
Abstract
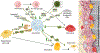
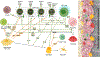
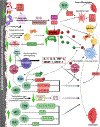
Osteoimmunology is at full display during endosseous implant osseointegration. Bone formation, maintenance and resorption at the implant surface is a result of bidirectional and dynamic reciprocal communication between the bone and immune cells that extends beyond the well-defined osteoblast-osteoclast signaling. Implant surface topography informs adherent progenitor and immune cell function and their cross-talk to modulate the process of bone accrual. Integrating titanium surface engineering with the principles of immunology is utilized to harness the power of immune system to improve osseointegration in healthy and diseased microenvironments. This review summarizes current information regarding immune cell-titanium implant surface interactions and places these events in the context of surface-mediated immunomodulation and bone regeneration. A mechanistic approach is directed in demonstrating the central role of osteoimmunology in the process of osseointegration and exploring how regulation of immune cell function at the implant-bone interface may be used in future control of clinical therapies. The process of peri-implant bone loss is also informed by immunomodulation at the implant surface. How surface topography is exploited to prevent osteoclastogenesis is considered herein with respect to peri-implant inflammation, osteoclastic precursor-surface interactions, and the upstream/downstream effects of surface topography on immune and progenitor cell function.
Keywords: BMP-2; Immunoengineering; Implant surface topography; Macrophage; Nano; Oncostatin M; Roughness.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



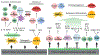





Similar articles
-
Topography Influences Adherent Cell Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis.J Dent Res. 2016 Mar;95(3):319-26. doi: 10.1177/0022034515616760. Epub 2015 Nov 9. J Dent Res. 2016. PMID: 26553885 Free PMC article.
-
A role for surface topography in creating and maintaining bone at titanium endosseous implants.J Prosthet Dent. 2000 Nov;84(5):522-34. doi: 10.1067/mpr.2000.111966. J Prosthet Dent. 2000. PMID: 11105008 Review.
-
Effect of the immune responses induced by implants in a integrated three-dimensional micro-nano topography on osseointegration.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021 Aug;109(8):1429-1440. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.37134. Epub 2020 Dec 11. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021. PMID: 33253467
-
Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: current knowledge and open questions.Periodontol 2000. 2017 Feb;73(1):22-40. doi: 10.1111/prd.12179. Periodontol 2000. 2017. PMID: 28000277 Review.
-
In vivo monitoring of the bone healing process around different titanium alloy implant surfaces placed into fresh extraction sockets.J Dent. 2012 Apr;40(4):338-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2012.01.010. Epub 2012 Jan 28. J Dent. 2012. PMID: 22307025
Cited by
-
Tissue Engineering Supporting Regenerative Strategies to Enhance Clinical Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopaedics: A Scoping, Perspective Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 6;11(3):795. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030795. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Light-Responsive Liquid Crystal Surface Topographies for Dynamic Stimulation of Cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 May 14;17(19):27871-27881. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c02526. Epub 2025 May 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40318038 Free PMC article.
-
UTX Responds to Nanotopography to Suppress Macrophage Inflammatory Response by Remodeling H3K27me3 Modification.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Aug;12(29):e05723. doi: 10.1002/advs.202505723. Epub 2025 May 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40386877 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional micro/nano-textured titanium with bactericidal, osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties: Insights from in vitro and in vivo studies.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Mar 27;32:101710. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101710. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40230651 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immune microenvironments by polyetheretherketone surface topography for improving osseointegration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Mar 11;23(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03272-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40069791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooper LF, Shirazi S, Osseointegration—the biological reality of successful dental implant therapy: a narrative review, Front. Oral Maxillof. Med (2022), 10.21037/fomm-21-77. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

