A prospective study on the prevalence of NAFLD, advanced fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in people with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 36410554
- PMCID: PMC9975077
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.11.010
A prospective study on the prevalence of NAFLD, advanced fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in people with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background & aims: There are limited prospective data on patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) specifically enrolled and systematically assessed for advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis due to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the prevalence of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in a prospectively recruited cohort of adults with T2DM.
Methods: This prospective study enrolled adults aged ≥50 years with T2DM, recruited from primary care or endocrinology clinics. Participants underwent a standardized clinical research visit with MRI-proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF), magnetic resonance elastography (MRE), vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) and controlled-attenuation parameter. NAFLD was defined as MRI-PDFF ≥5% after exclusion of other liver diseases. Advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis were defined by established liver stiffness cut-off points on MRE or VCTE if MRE was not available.
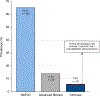
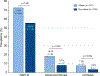
Results: Of 524 patients screened, 501 adults (63% female) with T2DM met eligibility. The mean age and BMI were 64.6 (±8.1) years and 31.4 (±5.9) kg/m2, respectively. The prevalence of NAFLD, advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis was 65%, 14% and 6%, respectively. In multivariable adjusted models, adjusted for age and sex, obesity and insulin use were associated with increased odds of advanced fibrosis (odds ratio 2.50; 95% CI 1.38-4.54; p = 0.003 and odds ratio 2.71; 95% CI 1.33-5.50; p = 0.006, respectively). Among 29 patients with cirrhosis, two were found to have hepatocellular carcinoma and one patient had gallbladder adenocarcinoma.
Conclusion: Utilizing a uniquely well-phenotyped prospective cohort of patients aged ≥50 years with T2DM, we found that the prevalence of advanced fibrosis was 14% and that of cirrhosis was 6%. These data underscore the high risk of advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis in adults aged ≥50 years with T2DM.
Impact and implications: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is common in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM), however, there are limited prospective data characterizing the prevalence of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis using the most accurate non-invasive biomarkers of liver fat and fibrosis. We show that 14% of older adults with T2DM have advanced fibrosis and 6% have cirrhosis, which places them at risk for liver failure and liver cancer. Accurate prevalence rates and comparative analysis regarding the diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests in this population will guide the optimal screening strategy and future cost-effectiveness analyses. These results will inform future Hepatology and Endocrinology practice guidelines regarding NAFLD screening programs in older adults with T2DM.
Keywords: diabetes; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; screening.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests
RL serves as a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Anylam/Regeneron, Amgen, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myer Squibb, CohBar, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gilead, Glympse bio, Hightide, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen Inc., Madrigal, Metacrine, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, Theratechnologies, 89 bio, Terns Pharmaceuticals and Viking Therapeutics. In addition his institutions received research grants from Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Astrazeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galectin Therapeutics, Galmed Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Intercept, Hanmi, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Merck, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sonic Incytes and Terns Pharmaceuticals. Co-founder of LipoNexus Inc.
Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further.
Figures

Comment in
-
Screening for NAFLD and its severity in type 2 diabetic patients: Value of magnetic resonance imaging and outstanding issues.J Hepatol. 2023 May;78(5):e166-e167. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.12.004. Epub 2022 Dec 14. J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36528235 No abstract available.
-
Reply to: "Screening for NAFLD and its severity in type 2 diabetic patients: Value of magnetic resonance imaging and outstanding issues".J Hepatol. 2023 May;78(5):e168-e169. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.01.022. Epub 2023 Feb 1. J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36736737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Advancing towards accurate phenotyping based on metabolic and fibrosis risk in metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease: one step closer to personalized care.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024 Feb 1;13(1):128-131. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-563. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38322230 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2016;64:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Loomba R, Wong R, Fraysse J, Shreay S, Li S, Harrison S, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression rates to cirrhosis and progression of cirrhosis to decompensation and mortality: a real world analysis of medicare data. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;51:1149–1159. - PubMed
-
- McPherson S, Hardy T, Henderson E, Burt AD, Day CP, Anstee QM. Evidence of NAFLD progression from steatosis to fibrosing-steatohepatitis using paired biopsies: implications for prognosis and clinical management. J Hepatol 2015;62:1148–1155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

