Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals in Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh 2020: a population-based cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36410810
- PMCID: PMC9679871
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066653
Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals in Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh 2020: a population-based cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objectives: The study aimed to determine the seroprevalence, the fraction of asymptomatic infections, and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 infections among the Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals (FDMNs).
Design: It was a population-based two-stage cross-sectional study at the level of households.
Setting: The study was conducted in December 2020 among household members of the FDMN population living in the 34 camps of Ukhia and Teknaf Upazila of Cox's Bazar district in Bangladesh.
Participants: Among 860 697 FDMNs residing in 187 517 households, 3446 were recruited for the study. One individual aged 1 year or older was randomly selected from each targeted household.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Blood samples from respondents were tested for total antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 using Wantai ELISA kits, and later positive samples were validated by Kantaro kits.
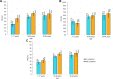
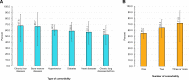
Results: More than half (55.3%) of the respondents were females, aged 23 median (IQR 14-35) years and more than half (58.4%) had no formal education. Overall, 2090 of 3446 study participants tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibody. The weighted and test adjusted seroprevalence (95% CI) was 48.3% (45.3% to 51.4%), which did not differ by the sexes. Children (aged 1-17 years) had a significantly lower seroprevalence 38.6% (95% CI 33.8% to 43.4%) compared with adults (58.1%, 95% CI 55.2% to 61.1%). Almost half (45.7%, 95% CI 41.9% to 49.5%) of seropositive individuals reported no relevant symptoms since March 2020. Antibody seroprevalence was higher in those with any comorbidity (57.8%, 95% CI 50.4% to 64.5%) than those without (47.2%, 95% CI 43.9% to 50.4%). Multivariate logistic regression analysis of all subjects identified increasing age and education as risk factors for seropositivity. In children (≤17 years), only age was significantly associated with the infection.
Conclusions: In December 2020, about half of the FDMNs had antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, including those who reported no history of symptoms. Periodic serosurveys are necessary to recommend appropriate public health measures to limit transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; EPIDEMIOLOGY; Epidemiology; PUBLIC HEALTH; Public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Misconceptions about COVID-19 among older Rohingya (forcefully displaced Myanmar nationals) adults in Bangladesh: findings from a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2021 May 28;11(5):e050427. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-050427. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34049923 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of scabies and its associated environmental risk factors among the Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals living in the Cox's Bazar district of Bangladesh.J Migr Health. 2024 Feb 27;9:100220. doi: 10.1016/j.jmh.2024.100220. eCollection 2024. J Migr Health. 2024. PMID: 39263380 Free PMC article.
-
Oral cholera vaccine coverage evaluation survey: Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals and host community in Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 5;11:1147563. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1147563. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37475769 Free PMC article.
-
Difficulties faced by older Rohingya (forcibly displaced Myanmar nationals) adults in accessing medical services amid the COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh.BMJ Glob Health. 2021 Dec;6(12):e007051. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2021-007051. BMJ Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34903566 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of a killed bivalent whole cell oral cholera vaccine in forcibly displaced Myanmar nationals in Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Mar 16;14(3):e0007989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007989. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32176695 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in wet market workers in Dhaka, Bangladesh in 2022.IJID Reg. 2024 Nov 24;14:100497. doi: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2024.100497. eCollection 2025 Mar. IJID Reg. 2024. PMID: 39810749 Free PMC article.
-
"Everything had stopped, no meeting, no gathering": Social interactions during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2025 May 27;20(5):e0323108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323108. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40424392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): situation report, 11. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): serology, antibodies and immunity. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/coronavirus-dis... [Accessed 2021].
-
- World Health Organization . Population-Based age-stratified seroepidemiological investigation protocol for COVID-19 virus infection. World Health Organization, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
