Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism engages memory-associated systems to augment olfaction
- PMID: 36411369
- PMCID: PMC9678911
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-24365-5
Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism engages memory-associated systems to augment olfaction
Abstract
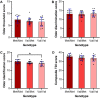
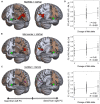
The neurogenetic basis of variability in human olfactory function remains elusive. This study examined olfactory performance and resting-state functional neuroimaging results from healthy volunteers within the context of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) val66met polymorphism with the aim of unraveling the genotype-associated intrinsic reorganization of the olfactory network. We found that the presence of the Met allele is associated with better olfactory identification and additional engagement of semantic memory system within the olfactory network, in an allele dosage-dependent manner. This suggests that the Met allele may promote adaptive neural reorganization to augment olfactory capacity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- V108B-025/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V110C-035/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- 108-V-B-021/Taipei Veterans General Hospital -National Yang-Ming University Excellent Physician-Scientist Cultivation Program
- MOST 108-2314-B-075-012/Ministry of Science and Technology
- MOST 109-2314-B-010-037-MY2/Ministry of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

