Distinct mechanisms of CB1 and GABAB receptor presynaptic modulation of striatal indirect pathway projections to mouse globus pallidus
- PMID: 36412169
- PMCID: PMC10107704
- DOI: 10.1113/JP283614
Distinct mechanisms of CB1 and GABAB receptor presynaptic modulation of striatal indirect pathway projections to mouse globus pallidus
Abstract
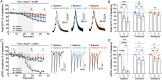
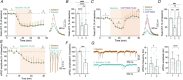
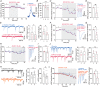
Presynaptic modulation is a fundamental process regulating synaptic transmission. Striatal indirect pathway projections originate from A2A-expressing spiny projection neurons (iSPNs), targeting the globus pallidus external segment (GPe) and control the firing of the tonically active GPe neurons via GABA release. It is unclear if and how the presynaptic G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), GABAB and CB1 receptors modulate iSPN-GPe projections. Here we used an optogenetic platform to study presynaptic Ca2+ and GABAergic transmission at iSPN projections, using a genetic strategy to express the calcium sensor GCaMP6f or the excitatory channelrhodopsin (hChR2) on iSPNs. We found that P/Q-type calcium channels are the primary voltage-gated Ca2+ channel (VGCC) subtype controlling presynaptic calcium and GABA release at iSPN-GPe projections. N-type and L-type VGCCs also contribute to GABA release at iSPN-GPe synapses. GABAB receptor activation resulted in a reversible inhibition of presynaptic Ca2+ transients (PreCaTs) and an inhibition of GABAergic transmission at iSPN-GPe synapses. CB1 receptor activation did not inhibit PreCaTs but inhibited GABAergic transmission at iSPN-GPe projections. CB1 effects on GABAergic transmission persisted in experiments where NaV and KV 1 were blocked, indicating a VGCC- and KV 1-independent presynaptic mechanism of action of CB1 receptors. Taken together, presynaptic modulation of iSPN-GPe projections by CB1 and GABAB receptors is mediated by distinct mechanisms. KEY POINTS: P/Q-type are the predominant voltage-gated Ca2+ channels controlling presynaptic Ca2+ and GABA release on the striatal indirect pathway projections. GABAB receptors modulate iSPN-GPe projections via a VGCC-dependent mechanism. CB1 receptors modulate iSPN-GPe projections via a VGCC-independent mechanism.
Keywords: basal ganglia; calcium imaging; neurotransmitter release; optogenetics; presynaptic.
Published 2022. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. The Journal of Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Striatal Direct and Indirect Pathway Output Structures Are Differentially Altered in Mouse Models of Huntington's Disease.J Neurosci. 2018 May 16;38(20):4678-4694. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0434-18.2018. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29691329 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced striatopallidal gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)A receptor transmission in mouse models of huntington's disease.Mov Disord. 2019 May;34(5):684-696. doi: 10.1002/mds.27622. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Mov Disord. 2019. PMID: 30726572
-
Inhibition of Nigrostriatal Dopamine Release by Striatal GABAA and GABAB Receptors.J Neurosci. 2019 Feb 6;39(6):1058-1065. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2028-18.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30541909 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic neurotransmission in globus pallidus and its involvement in neurologic disorders.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2004 Aug 25;56(4):427-35. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15322674 Review.
-
GABA(B) and group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the striatopallidal complex in primates.J Anat. 2000 May;196 ( Pt 4)(Pt 4):555-76. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2000.19640555.x. J Anat. 2000. PMID: 10923987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A non-canonical striatopallidal "Go" pathway that supports motor control.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 11:rs.3.rs-2524816. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2524816/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 23;14(1):6712. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42288-1. PMID: 36798372 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Spontaneous Activity of the Local GABAergic Synaptic Network Causes Irregular Neuronal Firing in the External Globus Pallidus.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 22;43(8):1281-1297. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1969-22.2023. Epub 2023 Jan 9. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36623877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonm, A. V. , Elezgarai, I. , Gremel, C. M. , Viray, K. , Bamford, N. S. , Palmiter, R. D. , Grandes, P. , Lovinger, D. M. , & Stella, N. (2021). Control of exploration, motor coordination and amphetamine sensitization by cannabinoid CB 1 receptors expressed in medium spiny neurons. European Journal of Neuroscience, 54, 4934–4952. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

