17β-estradiol Enhances 5-Fluorouracil Anti-Cancer Activities in Colon Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 36412903
- PMCID: PMC9680382
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci10040062
17β-estradiol Enhances 5-Fluorouracil Anti-Cancer Activities in Colon Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
Background: 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) represents one of the major constituents of chemotherapy combination regimens in colon cancer (CRC) treatments; however, this regimen is linked with severe adverse effects and chemoresistance. Thus, developing more efficient approaches for CRC is urgently needed to overcome these problems and improve the patient survival rate. Currently, 17β-estradiol (E2) has gained greater attention in colon carcinogenesis, significantly lowering the incidence of CRC in females at reproductive age compared with age-matched males.
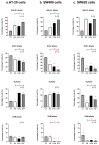
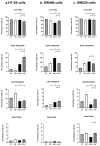
Aims: This study measured the effects of E2 and/or 5-FU single/dual therapies on cell cycle progression and apoptosis against human HT-29 female and SW480 male primary CRC cells versus their impact on SW620 male metastatic CRC cells.
Methods: The HT-29, SW480, and SW620 cells were treated with IC50 of E2 (10 nM) and 5-FU (50 μM), alone or combined (E+F), for 48 h before cell cycle and apoptosis analyses using flow cytometry.
Results: The data here showed that E2 monotherapy has great potential to arrest the cell cycle and induce apoptosis in all the investigated colon cancer cells, with the most remarkable effects on metastatic cells (SW620). Most importantly, the dual therapy (E+F) has exerted anti-cancer activities in female (HT-29) and male (SW480) primary CRC cells by inducing apoptosis, which was preferentially provoked in the sub-G1 phase. However, the dual treatment showed the smallest effect in SW620 metastatic cells.
Conclusion: this is the first study that demonstrated that the anti-cancer actions of 17β-estradiol and 5-Fluorouracil dual therapy were superior to the monotherapies in female and male primary CRC cells; it is proposed that this treatment strategy could be promising for the early stages of CRC. At the same time, 17β-estradiol monotherapy could be a better approach for treating the metastatic forms of the disease. Nevertheless, additional investigations are still required to determine their precise therapeutic values in CRC.
Keywords: 17β-estradiol; 5-Fluorouracil; apoptosis; cell cycle; colon cancer cells; sub-G1 phase.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
17β-estradiol in colorectal cancer: friend or foe?Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 19;22(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01745-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39030619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced in vitro tumoricidal effects of 5-Fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and active vitamin D3 triple therapy against colon cancer cells by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Life Sci. 2022 May 1;296:120442. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120442. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35245520
-
Enhanced anti-cancer effects of oestrogen and progesterone co-therapy against colorectal cancer in males.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 3;13:941834. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.941834. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36263327 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo and In Vitro Enhanced Tumoricidal Effects of Metformin, Active Vitamin D3, and 5-Fluorouracil Triple Therapy against Colon Cancer by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR Network.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;14(6):1538. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061538. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326689 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Derived Alkaloids as a Potential Source of Treatment for Colorectal Cancer over the Past Five Years: A Comprehensive Review.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 29;13(19):2723. doi: 10.3390/plants13192723. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
17β-estradiol in colorectal cancer: friend or foe?Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 19;22(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01745-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39030619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genistein Enhances TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis Through the Inhibition of XIAP and DcR1 in Colon Carcinoma Cells Treated with 5-Fluorouracil.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2024 Mar 25;21(1):7-24. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2023.60543. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38528786 Free PMC article.
-
ERO1α regulates colon cancer progression and 5-FU resistance through the miR-451a/ARF1 axis.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2025 Aug 21;40(1):184. doi: 10.1007/s00384-025-04987-7. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2025. PMID: 40835727 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in colorectal cancer: with a focus on sex hormone-gut microbiome axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Mar 7;22(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01549-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38454453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct and indirect effects of estrogens, androgens and intestinal microbiota on colorectal cancer.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Nov 26;14:1458033. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1458033. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39660281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Globocan Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide 2020. [(accessed on 15 September 2022)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/%20data/factsheets/populations/900-world-fact-....
-
- Filipits M., Pirker R., Dunant A., Lantuejoul S., Schmid K., Huynh A., Haddad V., Andre F., Stahel R., Pignon J.-P., et al. Cell Cycle Regulators and Outcome of Adjuvant Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Completely Resected Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial Biologic Program. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007;25:2735–2740. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.08.2867. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brough R., Bajrami I., Vatcheva R., Natrajan R., Reis-Filho J.S., Lord C.J., Ashworth A. APRIN is a cell cycle specific BRCA2-interacting protein required for genome integrity and a predictor of outcome after chemotherapy in breast cancer. EMBO J. 2012;31:1160–1176. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.490. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

