Camptothesome Potentiates PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Improved Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Immunochemotherapy
- PMID: 36413426
- PMCID: PMC9744414
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00701
Camptothesome Potentiates PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Improved Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Immunochemotherapy
Abstract
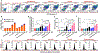
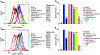
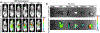
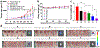
In this study, we focus on investigating the therapeutic effects of camptothesome on treating metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). We elucidate that camptothesome elicited stronger immunogenic cell death (ICD) compared to free camptothecin (CPT) and Onivyde in 4T1 TNBC cells. In addition, camptothesome is mainly internalized by the 4T1 and MDA-MB-231 cells through clathrin-mediated endocytosis based on the results of flow cytometry. Through real-time Lago optical imaging, camptothesome shows excellent tumor-targeting efficiency in orthotopic TNBC tumors. We demonstrate that camptothesome can upregulate programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in 4T1 tumors in an interferon gamma (IFN-γ)-dependent manner. Furthermore, the anti-TNBC efficacy studies reveal that camptothesome is superior to Onivyde and markedly potentiates PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy with complete lung metastasis remission in an orthotopic 4T1-Luc2 tumor model. This combination therapy eliciting robust cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) response via boosting tumor-infiltrating cluster of differentiation 8 (CD8), calreticulin (CRT), high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB-1), low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), IFN-γ, and granzyme B. Our work corroborates the promise of camptothesome in favorably modulating tumor immune microenvironment via inducing ICD to fortify the PD-L1 checkpoint blockade therapy for improved treatment of intractable TNBC.
Keywords: camptothecin; camptothesome; immune checkpoint blockade; immunogenic cell death; nanovesicle; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
J.L. has applied for patents related to Camptothesome technology. The other authors have no competing interests.
Figures
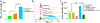

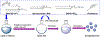
References
-
- Kwa MJ; Adams S Checkpoint inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): Where to go from here. Cancer 2018, 124 (10), 2086–2103. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L; Wang XI; Ding J; Sun Q; Zhang S The predictive and prognostic value of Foxp3+/CD25+ regulatory T cells and PD-L1 expression in triple negative breast cancer. Ann Diagn Pathol 2019, 40, 143–151. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Nunez I; Rozalen C; Palomeque JA; Sangrador I; Dalmau M; Comerma L; Hernandez-Prat A; Casadevall D; Menendez S; Liu DD; et al. LCOR mediates interferon-independent tumor immunogenicity and responsiveness to immune-checkpoint blockade in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Cancer 2022, 3 (3), 355–370. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P; Kimler BF; O’Dea A; Nye L; Wang YY; Yoder R; Staley JM; Prochaska L; Wagner J; Amin AL; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Anthracycline-free and Anthracycline-containing Neoadjuvant Carboplatin Chemotherapy Regimens in Stage I-III Triple-negative Breast Cancer (NeoSTOP). Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2021, 27 (4), 975–982. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

