CD6-mediated inhibition of T cell activation via modulation of Ras
- PMID: 36414966
- PMCID: PMC9682754
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-022-00998-x
CD6-mediated inhibition of T cell activation via modulation of Ras
Abstract
Background: CD6 is one of many cell surface receptors known to regulate signal transduction upon T cell activation. However, whether CD6 mediates costimulatory or inhibitory signals is controversial. When T cells engage with antigen presenting cells (APCs), CD6 interacts with its ligand CD166 at the cell-cell interface while the cytosolic tail assembles a complex signalosome composed of adaptors and effector enzymes, that may either trigger activating signaling cascades, or instead modulate the intensity of signaling. Except for a few cytosolic adaptors that connect different components of the CD6 signalosome, very little is known about the mechanistic effects of the cytosolic effectors that bind CD6.
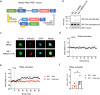
Methods: Jurkat model T cells were transfected to express wild-type (WT) CD6, or a cytoplasmic truncation, signaling-disabled mutant, CD6Δcyt. The two resulting cell lines were directly activated by superantigen (sAg)-loaded Raji cells, used as APCs, to assess the net signaling function of CD6. The Jurkat cell lines were further adapted to express a FRET-based unimolecular HRas biosensor that reported the activity of this crucial GTPase at the immunological synapse.
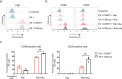
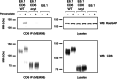
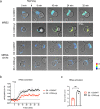
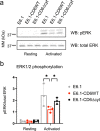
Results: We show that deletion of the cytosolic tail of CD6 enhances T-cell responses, indicating that CD6 restrains T-cell activation. One component of the CD6-associated inhibitory apparatus was found to be the GTPase activating protein of Ras (RasGAP), that we show to associate with CD6 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. The FRET HRas biosensor that we developed was demonstrated to be functional and reporting the activation of the T cell lines. This allowed to determine that the presence of the cytosolic tail of CD6 results in the down-regulation of HRas activity at the immunological synapse, implicating this fundamental GTPase as one of the targets inhibited by CD6.
Conclusions: This study provides the first description of a mechanistic sequence of events underlying the CD6-mediated inhibition of T-cell activation, involving the modulation of the MAPK pathway at several steps, starting with the coupling of RasGAP to the CD6 signalosome, the repression of the activity of Ras, and culminating in the reduction of ERK1/2 phosphorylation and of the expression of the T-cell activation markers CD69 and IL-2R α chain. Video abstract.
Keywords: Cell surface molecules; FRET; GTPases; Immunological synapse; Inhibitory receptors; Signaling transduction.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The lymphocyte receptor CD6 interacts with syntenin-1, a scaffolding protein containing PDZ domains.J Immunol. 2005 Aug 1;175(3):1406-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.3.1406. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16034076
-
CD6, a Rheostat-Type Signalosome That Tunes T Cell Activation.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 18;9:2994. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02994. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activation by the CD6 lymphocyte surface receptor.J Immunol. 2006 Jul 15;177(2):1152-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.1152. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16818773
-
CD6 attenuates early and late signaling events, setting thresholds for T-cell activation.Eur J Immunol. 2012 Jan;42(1):195-205. doi: 10.1002/eji.201040528. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Eur J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21956609 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning T Cell Activation: The Function of CD6 At the Immunological Synapse and in T Cell Responses.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(6):630-9. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150531152439. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26028048 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting CDCP1 boost CD8+ T cells-mediated cytotoxicity in cervical cancer via the JAK/STAT signaling pathway.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Oct 24;12(10):e009416. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009416. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39455095 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Characteristics of Coarse Feeding Tolerance of Ding'an Pigs: Phenotypic and Candidate Genes Identification.Genes (Basel). 2024 May 8;15(5):599. doi: 10.3390/genes15050599. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790227 Free PMC article.
-
Ligands of CD6: roles in the pathogenesis and treatment of cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1528478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1528478. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39840036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The OT-II model reveals dual in vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory properties of CD6 in T cell activation.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1571590. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1571590. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40642095 Free PMC article.
-
CD6 in Human Disease.Cells. 2025 Feb 13;14(4):272. doi: 10.3390/cells14040272. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39996744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kamoun M, Kadin ME, Martin PJ, Nettleton J, Hansen JA. A novel human T cell antigen preferentially expressed on mature T cells and shared by both well and poorly differentiated B cell leukemias and lymphomas. J Immunol. 1981;127(3):987–991. - PubMed
-
- Endres N, Riethmueller G, Rieber EP. Functional characterization of a novel B-cell subset defined by the CD6 antigen. In: Knapp W, Dörken B, Gilks WR, Rieber EP, Schmidt RE, Stein H, Borne AEGKvd, editors. Leukocyte typing IV: white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1989. p. 340.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

