First wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Madrid: handling the unexpected in a tertiary hospital
- PMID: 36415301
- PMCID: PMC9648550
- DOI: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2022.63.3.2037
First wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Madrid: handling the unexpected in a tertiary hospital
Abstract
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic was declared on March 11th, 2020. By the end of January, the first imported cases were detected in Spain and, by March, the number of cases was growing exponentially, causing the implementation of a national lockdown. Madrid has been one of the most affected regions in terms of both cases and deaths. The aim of this study is to describe the epidemic curve and the epidemiological features and outcomes of COVID-19 patients hospitalized in La Paz University Hospital, a tertiary hospital located in Madrid.
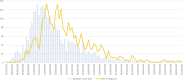
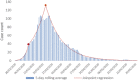
Methods: We included confirmed and probable COVID-19 cases admitted to our centre from February 26th to June 1st, 2020. We studied trends in hospitalization and ICU admissions using joinpoint regression analysis.
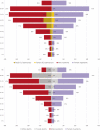
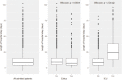
Results: A sample of 2970 patients was obtained. Median age was 70 years old (IQR 55-82) and 54.8% of them were male. ICU admission rate was 8.7% with a mortality rate of 45.7%. Global CFR was 21.8%. Median time from symptom onset to death was 14 days (IQR 9-22).
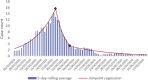
Conclusions: We detected an admissions peak on March 21st followed by a descending trend, matching national and regional data. Age and sex distribution were comparable to further series nationally and in western countries.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemic curve; Pandemic; SARS-CoV-2.
©2022 Pacini Editore SRL, Pisa, Italy.
Figures

References
-
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Situation Reports n.d. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... (Accessed on: June 1, 2020).
-
- Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen Y-M, Wang W, Song Z-G, Hu Y, Tao Z-W, Tian J-H, Pei Y-Y, Yuan M-L, Zhang Y-L, Dai F-H, Liu Y, Wang Q-M, Zheng J-J, Xu L, Holmes EC, Zhang Y-Z. A New Coronavirus Associated with Human Respiratory Disease in China. Nature 2020;579:265-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) events as they happen n.d. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a... (Accessed on: June 1, 2020).
-
- Guan W, Ni Z, Hu Y, Liang W, Ou C, He J, Liu L, Shan H, Lei C, Hui DSC, Du B, Li L, Zeng G, Yuen K-Y, Chen R, Tang C, Wang T, Chen P, Xiang J, Li S, Wang J, Liang Z, Peng Y, Wei L, Liu Y, Hu Y, Peng P, Wang J, Liu J, Chen Z, Li G, Zheng Z, Qiu S, Luo J, Ye C, Zhu S, Zhong N. Clinical characteristics of Coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med 2020;382:1708-20. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study - The Lancet n.d. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-67362030211-7... (Accessed on: October 9, 2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
