A Comparative Analysis Between Ultrasound and Electromyographic and Nerve Conduction Studies in Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36415360
- PMCID: PMC9674040
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.30476
A Comparative Analysis Between Ultrasound and Electromyographic and Nerve Conduction Studies in Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
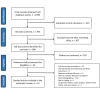
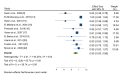
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common upper extremity neuropathy. The disease initially manifests as a sensory disorder in the form of paresthesia, numbness, or tingling of the fingers. The diagnosis is usually made based on history and clinical symptoms, which are confirmed using nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography. More recently, ultrasound has gained more use in CTS diagnosis due to its advantages, which include patients' comfort during diagnosis, better visualization of anatomy and nerve forms directly, and cost-effectiveness. However, a literature review shows that the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound over NCS is still in question; therefore, the present systematic review was carried out to compare the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound to NCS and electromyography. A systematic literature search was performed on five electronic databases: PubMed, Medline, Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar. The search strategy limited the retrieval of literature published between 2000 and 2022. Of the 1098 articles retrieved from the electronic databases, only 12 met the inclusion criteria. A meta-analysis of outcomes from the included studies showed that the pooled sensitivity and specificity of the ultrasound were 0.80 (95% CI: 0.73, 0.88) and 0.90 (0.83, 0.96), respectively. On the other hand, combing the outcomes of electromyography and NCS resulted in sensitivity and specificity values of 0.89 (95% CI: 0.84, 0.95) and 0.77 (95% CI; 0.64, 0.90), respectively. The results show that ultrasound has comparable sensitivity and slightly higher specificity than NCS and electromyography; therefore, ultrasound can be used as an alternative diagnostic test for CTS. However, it cannot replace NCS and electromyography since more research needs to be done on doubtful and secondary cases of CTS.
Keywords: carpal tunnel syndrome; electrodiagnostic test; electromyography and electro-stimulation; high-resolution sonography; nerve conduction studies (ncs); systematic review and meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2022, Zaki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Carpal tunnel syndrome. LeBlanc KE, Cestia W. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2011/0415/p952.html. Am Fam Physician. 2011;83:952–958. - PubMed
-
- Evidence-based guideline: neuromuscular ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Cartwright MS, Hobson-Webb LD, Boon AJ, et al. Muscle Nerve. 2012;46:287–293. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
