The Y-Pelvic Osteotomy in Treating Bladder Exstrophy: A Surgical Technique
- PMID: 36415431
- PMCID: PMC9674189
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.30520
The Y-Pelvic Osteotomy in Treating Bladder Exstrophy: A Surgical Technique
Abstract
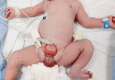
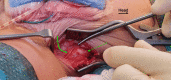
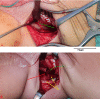
Bladder exstrophy (BE) is a rare congenital anomaly caused by an embryological defect in the closure of the abdominal wall. It comprises a spectrum of defects about severity, including epispadias in the mildest form and cloacal exstrophy in the worst. Surgical correction is required to achieve urinary continence, maintain normal renal function, achieve secured abdominal wall closure, and create cosmetically and functionally satisfactory genitalia. Iliac bone osteotomy is considered essential to achieve the above goals in most patients by reducing the tension of the closed abdominal wall layers, particularly when present late in infancy. Several types of pelvic iliac bone osteotomy have been described to aid bladder and cloacal exstrophy closure. They can be grouped into posterior iliac osteotomy, anterior iliac osteotomy, oblique (also called diagonal) iliac osteotomy, and a combination of posterior and anterior iliac osteotomy. We described here the Y-pelvic osteotomy, which was developed by the Manchester Orthopaedic Group in the United Kingdom. It has the advantage of anterior and posterior osteotomies but also has less risk to the neurovascular structures, less blood loss, and ease of surgical technique. The osteotomy was named the Y-pelvic osteotomy due to the morphological shape it resembles.
Keywords: bladder reconstruction; cloacal exstrophy; epispadias and bladder exstrophy; pelvis osteotomy; persistent cloaca.
Copyright © 2022, Alshryda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bilateral Anterior Innominate Osteotomy for Bladder Exstrophy.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2019 Jan 9;9(1):e1. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.18.00018. eCollection 2019 Mar 26. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2019. PMID: 31086719 Free PMC article.
-
One-stage external iliac fixation device and bilateral fascial and groin flaps facilitate abdominal wall closure after posterior sagittal iliac osteotomy in cloacal exstrophy.Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2011 Dec;21(6):377-80. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1287852. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2011. PMID: 22169988
-
Anterior innominate osteotomy in repair of bladder exstrophy.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001 Feb;83(2):184-93. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200102000-00005. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11216679
-
The exstrophy-epispadias complex.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009 Oct 30;4:23. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-23. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009. PMID: 19878548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classic bladder exstrophy: orthopaedic surgical considerations.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011 Sep;19(9):518-26. doi: 10.5435/00124635-201109000-00002. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011. PMID: 21885697 Review.
Cited by
-
A long-term outcome (up to 29 years) of bilateral iliac wings "bayonet osteotomies" for closure of bladder exstrophy.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 May 2;18(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03810-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37131198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anterior innominate osteotomy in repair of bladder exstrophy. Sponseller PD, Jani MM, Jeffs RD, Gearhart JP. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:184–193. - PubMed
-
- Anterior innominate osteotomies for failure or late closure of bladder exstrophy. Sponseller PD, Gearhart JP, Jeffs RD. J Urol. 1991;146:137–140. - PubMed
-
- Contemporary epidemiology of bladder exstrophy in the United States. Nelson CP, Dunn RL, Wei JT. J Urol. 2005;173:1728–1731. - PubMed
-
- Prospective study on the incidence of bladder/cloacal exstrophy and epispadias in Europe. Cervellione RM, Mantovani A, Gearhart J, Bogaert G, Gobet R, Caione P, Dickson AP. J Pediatr Urol. 2015;11:337–336. - PubMed
-
- The pelvis of fetuses in the exstrophy complex. Wakim A, Barbet JP, Lair-Milan F, Dubousset J. https://journals.lww.com/pedorthopaedics/Abstract/1997/05000/The_Pelvis_.... J Pediatr Orthop. 1997;17:402–405. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
