Use of Aminophylline to Reverse Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Critical Care Patients
- PMID: 36415773
- PMCID: PMC9674366
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-27.8.739
Use of Aminophylline to Reverse Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Critical Care Patients
Abstract
Objective: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a complication encountered in 18% to 51% of pediatric critical care patients admitted for treatment of other primary diagnoses and is an independent risk factor for increased morbidity and mortality. Aminophylline has shown promise as a medication to treat AKI, but published studies have shown conflicting results. Our study seeks to assess the reversal of AKI following the administration of aminophylline in critically ill pediatric patients.
Methods: We performed a single-institution retrospective chart review of pediatric inpatients who were diagnosed with AKI and subsequently treated with non-continuous dose aminophylline between January 2016 and December 2018. Data were collected beginning 2 days prior to the initial dose of aminophylline through completion of the 5-day aminophylline course.
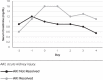
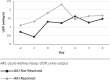
Results: Nineteen therapies among 17 patients were included in analysis. Twelve of the therapies resulted in resolution of AKI during the study period. We observed urine output increase of 19% (p = 0.0063) on the day following initiation of aminophylline therapy in the subset of patients whose AKI resolved. Trends toward decreased serum creatinine and lower inotropic support were also noted.
Conclusions: Based on these findings, aminophylline could be considered a potentially effective medication for use as rescue therapy in critically ill children with AKI. Limitations include small study population and retrospective nature. Further research in this area with a larger study population and a randomized control trial would allow for better characterization of the efficacy of aminophylline in reversal of AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; aminophylline; creatinine; critical care; diuretics; pediatric; vasoactive inotrope score.
Copyright. Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email membershipo@pediatricpharmacy.org 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures. The authors declare no conflicts or financial interest in any product or service mentioned in the manuscript, including grants, equipment, medications, employment, gifts, and honoraria.
Figures
References
-
- Selewski DT, Cornell TT, Heung M et al. Validation of the KDIGO acute kidney injury criteria in a pediatric critical care population. Intensive Care Med . 2014;40(10):1481–1488. - PubMed
-
- Alkandari O, Eddington KA, Hyder A et al. Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for pediatric intensive care unit mortality, longer length of stay and prolonged mechanical ventilation in critically ill children: a two-center retrospective cohort study. Crit Care . 2011;15(3):R146. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources