Variance-based sensitivity analysis of tuberculosis transmission models
- PMID: 36415976
- PMCID: PMC9682306
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0413
Variance-based sensitivity analysis of tuberculosis transmission models
Abstract
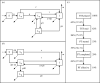
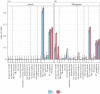
Mathematical models are widely used to provide evidence to inform policies for tuberculosis (TB) control. These models contain many sources of input uncertainty including the choice of model structure, parameter values and input data. Quantifying the role of these different sources of input uncertainty on the model outputs is important for understanding model dynamics and improving evidence for policy making. In this paper, we applied the Sobol sensitivity analysis method to a TB transmission model used to simulate the effects of a hypothetical population-wide screening strategy. We demonstrated how the method can be used to quantify the importance of both model parameters and model structure and how the analysis can be conducted on groups of inputs. Uncertainty in the model outputs was dominated by uncertainty in the intervention parameters. The important inputs were context dependent, depending on the setting, time horizon and outcome measure considered. In particular, the choice of model structure had an increasing effect on output uncertainty in high TB incidence settings. Grouping inputs identified the same influential inputs. Wider use of the Sobol method could inform ongoing development of infectious disease models and improve the use of modelling evidence in decision making.
Keywords: modelling; sensitivity analysis; tuberculosis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The predicted impact of tuberculosis preventive therapy: the importance of disease progression assumptions.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Nov 23;20(1):880. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05592-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33228580 Free PMC article.
-
Info-gap management of public health Policy for TB with HIV-prevalence and epidemiological uncertainty.BMC Public Health. 2012 Dec 19;12:1091. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-1091. BMC Public Health. 2012. PMID: 23249291 Free PMC article.
-
Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the basic reproductive rate. Tuberculosis as an example.Am J Epidemiol. 1997 Jun 15;145(12):1127-37. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009076. Am J Epidemiol. 1997. PMID: 9199543
-
Data needs for evidence-based decisions: a tuberculosis modeler's 'wish list'.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013 Jul;17(7):866-77. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.12.0573. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013. PMID: 23743307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of BCG vaccination policies among high-risk groups in low TB-burden countries: implications for vaccination strategy in Canadian indigenous communities.BMC Public Health. 2019 Nov 11;19(1):1504. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7868-9. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31711446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colijn C, Cohen T, Murray M. 2006. Mathematical models of tuberculosis: accomplishments and future challenges. In BIOMAT 2006: Int. Symp. on Mathematical and Computational Biology, Manaus, Brazil, 27–30 November. Singapore: World Scientific.
-
- Sanchez MA, Blower SM. 1997. Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the basic reproductive rate: tuberculosis as an example. AJE 145, 1127-1137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

