Nicotine-Mediated Rescue of α-Synuclein Toxicity Requires Synaptic Vesicle Glycoprotein 2 in Drosophila
- PMID: 36416213
- PMCID: PMC9974823
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.29283
Nicotine-Mediated Rescue of α-Synuclein Toxicity Requires Synaptic Vesicle Glycoprotein 2 in Drosophila
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by α-synuclein aggregation and loss of dopamine neurons. Risk of PD arises due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, which may interact, termed gene-environment (G×E) interactions. An inverse association between smoking and the risk of PD is well established, and a previous genome-wide G×E interaction study identified genetic variation in the synaptic-vesicle glycoprotein 2C (SV2C) locus as an important mediator of the degree to which smoking is inversely associated with PD.
Objective: We sought to determine the mechanism of the smoking-SV2C interaction in a Drosophila model of PD.
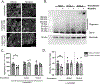
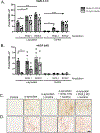
Methods: Flies expressing human α-synuclein in all neurons develop the hallmarks of PD, including motor dysfunction, loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons, and formation of α-synuclein inclusions. We assessed the effects of increasing doses of nicotine on these parameters of neurodegeneration, in the presence or absence of knockdown of two Drosophila orthologues of SV2, hereafter referred to as SV2L1 and SV2L2.
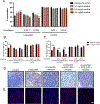
Results: The α-synuclein-expressing flies treated with nicotine had improved locomotion, DA neuron counts, and α-synuclein aggregation. However, in α-synuclein-expressing flies in which SV2L1 and SV2L2 were knocked down, nicotine failed to rescue neurodegeneration.
Conclusions: This work confirms a G×E interaction between nicotine and SV2, defines a role for this interaction in α-synuclein proteostasis, and suggests that future clinical trials on nicotine should consider genetic variation in SV2C. Furthermore, this provides proof of concept that our model can be used for the mechanistic study of G×E, paving the way for the investigation of additional G×E interactions or the identification of novel G×E. © 2022 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Drosophila; Gene-environment; Nicotine; Parkinson's disease; Synaptic; vesicle glycoprotein.
© 2022 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosures/COI concerning the current manuscript
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2C (SV2C) modulates dopamine release and is disrupted in Parkinson disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 14;114(11):E2253-E2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616892114. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28246328 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's disease risk genes act in glia to control neuronal α-synuclein toxicity.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Nov;159:105482. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105482. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 34390834 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic basis for the variable effect of smoking/nicotine on Parkinson's disease.Pharmacogenomics J. 2013 Dec;13(6):530-7. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2012.38. Epub 2012 Oct 2. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013. PMID: 23032990 Free PMC article.
-
The Overcrowded Crossroads: Mitochondria, Alpha-Synuclein, and the Endo-Lysosomal System Interaction in Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 25;20(21):5312. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215312. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31731450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cholesterol in α-Synuclein and Lewy Body Pathology in GBA1 Parkinson's Disease.Mov Disord. 2021 May;36(5):1070-1085. doi: 10.1002/mds.28396. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Mov Disord. 2021. PMID: 33219714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
α-Synuclein species in plasma neuron-derived extracellular vesicles as biomarkers for iRBD.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Nov;11(11):2891-2903. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52200. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39291779 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis reveals a conserved role for the amyloid precursor protein in proteostasis during aging.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 3;14(1):7034. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42822-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37923712 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Dopamine Homeostasis Associated with Alteration of Proteins in Synaptic Vesicles: A Putative Central Mechanism of Parkinson's Disease Pathogenesis.Aging Dis. 2024 May 7;15(3):1204-1226. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0821-2. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37815908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Protective Effects of Alkaloids against Alpha-synuclein Toxicity in Parkinson's Disease.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(2):112-127. doi: 10.2174/0113895575306884240604065754. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38874050 Review.
-
Synaptic Vesicle Glycoprotein 2C: a role in Parkinson's disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Sep 5;18:1437144. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1437144. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39301216 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

