Enzymatic Conjugation of Modified RNA Fragments by Ancestral RNA Ligase AncT4_2
- PMID: 36416557
- PMCID: PMC9746290
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.01679-22
Enzymatic Conjugation of Modified RNA Fragments by Ancestral RNA Ligase AncT4_2
Abstract
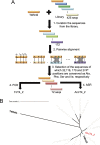
Oligonucleotide therapeutics have great potential as a next-generation approach to treating intractable diseases. Large quantities of modified DNA/RNA containing xenobiotic nucleic acids (XNAs) must be synthesized before clinical application. In this study, the ancestral RNA ligase AncT4_2 was designed by ancestral sequence reconstruction (ASR) to perform the conjugation reaction of modified RNA fragments. AncT4_2 had superior properties to native RNA ligase 2 from T4 phage (T4Rnl2), including high productivity, a >2.5-fold-higher turnover number, and >10°C higher thermostability. One remarkable point is the broad substrate selectivity of AncT4_2; the activity of AncT4_2 toward 17 of the modified RNA fragments was higher than that of T4Rnl2. The activity was estimated by measuring the conjugation reaction of two RNA strands, 3'-OH (12 bp) and 5'-PO4 (12 bp), in which the terminal and penultimate positions of the 3'-OH fragment and the first and second positions of the 5'-PO4 fragment were substituted by 2'-fluoro, 2'-O-methyl, 2'-O-methoxyethyl, and 2'-H, respectively. The enzymatic properties of AncT4_2 allowed the enzyme to conjugate large quantities of double-stranded RNA coding for patisiran (>400 μM level), which was formed by four RNA fragments containing 2'-OMe-substituted nucleic acids. Structural analysis of modeled AncT4_2 suggested that protein dynamics were changed by mutation to Gly or indel during ASR and that this may positively impact the conjugation of modified RNA fragments with the enzyme. AncT4_2 is expected to be a key biocatalyst in synthesizing RNA therapeutics by an enzymatic reaction. IMPORTANCE RNA therapeutics is one of the next-generation medicines for treating various diseases. Our designed ancestral RNA ligase AncT4_2 exhibited excellent enzymatic properties, such as high thermal stability, productivity, specific activity, and broad substrate selectivity compared to native enzymes. These advantages create the potential for AncT4_2 to be applied in conjugating the modified RNA fragments containing various xenobiotic nucleic acids. In addition, patisiran, a known polyneuropathy therapeutic, could be synthesized from four fragmented oligonucleotides at a preparative scale. Taken together, these findings indicate AncT4_2 could open the door to synthesizing RNA therapeutics by enzymatic reaction at large-scale production.
Keywords: RNA ligase; RNA therapeutics; ancestral sequence reconstruction; xenobiotic nucleic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Re-Engineering RNA Molecules into Therapeutic Agents.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Apr 16;52(4):1036-1047. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00650. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 30912917
-
Direct comparison of nick-joining activity of the nucleic acid ligases from bacteriophage T4.Biochem J. 2006 Aug 15;398(1):135-44. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060313. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16671895 Free PMC article.
-
Hybridization of 2'-ribose modified mixed-sequence oligonucleotides: thermodynamic and kinetic studies.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 May 15;29(10):2163-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.10.2163. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11353086 Free PMC article.
-
Modified nucleic acids: replication, evolution, and next-generation therapeutics.BMC Biol. 2020 Sep 2;18(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00803-6. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 32878624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xeno nucleic acids (XNAs) having non-ribose scaffolds with unique supramolecular properties.Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Mar 24;58(25):3993-4004. doi: 10.1039/d1cc05868a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022. PMID: 35107445 Review.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic potential of circular RNAs.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 Apr;26(4):230-244. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00806-x. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 39789148 Review.
-
Design of ancestral mammalian alkaline phosphatase bearing high stability and productivity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Dec 18;90(12):e0183124. doi: 10.1128/aem.01831-24. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39545738 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral sequence reconstruction as a tool for structural analysis of modular polyketide synthases.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 25;16(1):6847. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62168-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40715098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hammond SM, Hazell G, Shabanpoor F, Saleh AF, Bowerman M, Sleigh JN, Meijboom KE, Zhou H, Muntoni F, Talbot K, Gait MJ, Wood MJ. 2016. Systemic peptide-mediated oligonucleotide therapy improves long-term survival in spinal muscular atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:10962–10967. 10.1073/pnas.1605731113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

