Anti-tumor antibody isotype response can be modified with locally administered immunoadjuvants
- PMID: 36417163
- PMCID: PMC10238356
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-022-01258-8
Anti-tumor antibody isotype response can be modified with locally administered immunoadjuvants
Abstract
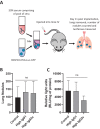
In situ vaccination with immunostimulatory compounds is a demonstrated means to treat tumors preclinically. While these therapeutic effects have been attributed to the actions of T cells or innate immune activation, characterisation of the humoral immune response is seldom performed. This study aims to identify whether the injection of immunoadjuvants, Addavax (Adda) and cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG), intratumorally can influence the antibody response. Specifically, whether intratumoral injection of immunoadjuvants can alter the tumor-specific antibody target, titre and isotype. Following this, the study aimed to investigate whether serum obtained from in situ vaccinated mice could neutralise circulating tumor cells. Serum was obtained from mice bearing B16F10-OVA-Luc-GFP tumors treated with immunoadjuvants. Antibody targets' titre and isotype were assessed by indirect ELISA. The ability of serum to neutralise circulating cancer cells was evaluated in a B16F10 pseudo-metastatic model. It was observed that tumor-bearing mice mount a specific anti-tumor antibody response. Antibody titre and target were unaffected by in situ vaccination with immunoadjuvants; however, a higher amount of IgG2c was produced in mice receiving Adda plus CpG. Serum from in situ vaccinated mice was unable to neutralise circulating B16F10 cells. Thus, this study has demonstrated that anti-tumor antibody isotype may be modified using in situ vaccination; however, this alone is not sufficient to neutralise circulating cancer cells.
Keywords: Antibody neutralisation; B16F10; CpG; Immunoadjuvants; In situ vaccination; Isotype.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

