Social Media Use and Mental Health: A Global Analysis
- PMID: 36417264
- PMCID: PMC9620890
- DOI: 10.3390/epidemiologia3010002
Social Media Use and Mental Health: A Global Analysis
Abstract
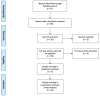
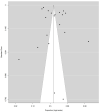
Research indicates that excessive use of social media can be related to depression and anxiety. This study conducted a systematic review of social media and mental health, focusing on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Based on inclusion criteria from the systematic review, a meta-analysis was conducted to explore and summarize studies from the empirical literature on the relationship between social media and mental health. Using PRISMA guidelines on PubMed and Google Scholar, a literature search from January 2010 to June 2020 was conducted to identify studies addressing the relationship between social media sites and mental health. Of the 39 studies identified, 20 were included in the meta-analysis. Results indicate that while social media can create a sense of community for the user, excessive and increased use of social media, particularly among those who are vulnerable, is correlated with depression and other mental health disorders.
Keywords: Facebook; Instagram; Twitter; mental health; social media; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mental Health Myths and Facts|MentalHealth.gov. [(accessed on 13 December 2021)];2020 Available online: https://www.mentalhealth.gov/basics/mental-health-myths-facts.
-
- Bashir H., Bhat S.A. Effects of Social Media on Mental Health: A Review. Int. J. Indian Psychol. 2017;4:125–131.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

