An autoactive NB-LRR gene causes Rht13 dwarfism in wheat
- PMID: 36417432
- PMCID: PMC9860330
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2209875119
An autoactive NB-LRR gene causes Rht13 dwarfism in wheat
Abstract
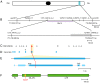
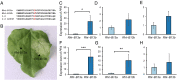
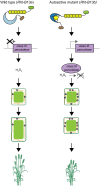
Semidwarfing genes have greatly increased wheat yields globally, yet the widely used gibberellin (GA)-insensitive genes Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b have disadvantages for seedling emergence. Use of the GA-sensitive semidwarfing gene Rht13 avoids this pleiotropic effect. Here, we show that Rht13 encodes a nucleotide-binding site/leucine-rich repeat (NB-LRR) gene. A point mutation in the semidwarf Rht-B13b allele autoactivates the NB-LRR gene and causes a height reduction comparable with Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b in diverse genetic backgrounds. The autoactive Rht-B13b allele leads to transcriptional up-regulation of pathogenesis-related genes including class III peroxidases associated with cell wall remodeling. Rht13 represents a new class of reduced height (Rht) gene, unlike other Rht genes, which encode components of the GA signaling or metabolic pathways. This discovery opens avenues to use autoactive NB-LRR genes as semidwarfing genes in a range of crop species, and to apply Rht13 in wheat breeding programs using a perfect genetic marker.
Keywords: Triticum aestivum L. (wheat); autoactive NB-LRR; reduced-height (Rht) gene; semidwarfing gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hedden P., The genes of the Green Revolution. Trends Genet. 19, 5–9 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Peng J., et al. , ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 400, 256–261 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Allan R. E., Influence of semidwarfism and genetic background on stand establishment of wheat. Crop Sci. 20, 634–638 (1980).
-
- Srinivasachary, et al. , Semi-dwarfing Rht-B1 and Rht-D1 loci of wheat differ significantly in their influence on resistance to Fusarium head blight. Theor. Appl. Genet. 118, 695–702 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

