Temporal progression of sepsis on critical care COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 36417653
- PMCID: PMC9683908
- DOI: 10.1590/1806-9282.20220669
Temporal progression of sepsis on critical care COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
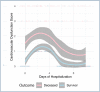
Objective: This study aimed to describe sepsis progression in critical COVID-19 patients using the SOFA score and investigate its relationship with mortality.
Methods: Three researchers collected and analyzed retrospective clinical and laboratory data found in electronic health records from all patients admitted to a severe COVID-19 exclusive intensive care unit from March 2020 to October 2020. Mixed-effect logistic regression was used to evaluate SOFA (Sepsis-3) score variables as mortality prediction markers, while Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to compare mortality between groups of patients. Cox proportional hazard models were used to further stratify mortality association between variants.
Results: A total of 73 patients were included. Temporal COVID-19-related sepsis progression analysis indicates difference in degrees and timing between different organ dysfunction over time. Sepsis-3 Cardiovascular Dysfunction characterized by severe hypotension added to the use of any vasopressor drugs was the only parameter associated with in-hospital death during the first 5 days of hospital admission (OR 2.19; 95%CI 1.14-4.20; p=0.01).
Conclusion: Increased Sepsis-3 Cardiovascular Dysfunction score, characterized as hypotension associated with the use of vasopressor drugs in the first days of intensive care unit stay, is related to higher mortality in COVID-19 patients and may be a useful prognostic prediction tool.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: the authors declare there is no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2022. [cited on May 6, 2022]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Alharthy A, Aletreby W, Faqihi F, Balhamar A, Alaklobi F, Alanezi K, et al. Clinical characteristics and predictors of 28-day mortality in 352 critically ill patients with COVID-19: a retrospective study. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021;11(1):98–104. doi: 10.2991/jegh.k.200928.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical