LINC00924-induced fatty acid metabolic reprogramming facilitates gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via hnRNPC-regulated alternative splicing of Mnk2
- PMID: 36418856
- PMCID: PMC9684446
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05436-x
LINC00924-induced fatty acid metabolic reprogramming facilitates gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via hnRNPC-regulated alternative splicing of Mnk2
Abstract
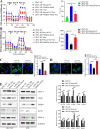
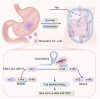
The molecular mechanism underlying gastric cancer (GC) peritoneal metastasis (PM) remains unclear. Here, we identified LINC00924 as a GC PM-related lncRNA through Microarray sequencing. LINC00924 was highly expressed in GC, and its high expression is associated with a broad range of PM. Via RNA sequencing, RNA pulldown assay, mass spectrometry, Seahorse, Lipidomics, spheroid formation and cell viability assays, we found that LINC00924 promoted fatty acid (FA) oxidation (FAO) and FA uptake, which was essential for matrix-detached GC cell survival and spheroid formation. Regarding the mechanism, LINC00924 regulated the alternative splicing (AS) of Mnk2 pre-mRNA by binding to hnRNPC. Specifically, LINC00924 enhanced the binding of hnRNPC to Mnk2 pre-mRNA at e14a, thus downregulating Mnk2a splicing and regulating the p38 MAPK/PPARα signaling pathway. Collectively, our results demonstrate that LINC00924 plays a role in promoting GC PM and could serve as a drug target.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Fujitani K, Yang HK, Mizusawa J, Kim YW, Terashima M, Han SU, et al. Gastrectomy plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric cancer with a single non-curable factor (REGATTA): a phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:309–18.. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00553-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

