Pathogenicity and virulence of malaria: Sticky problems and tricky solutions
- PMID: 36419237
- PMCID: PMC9815252
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2150456
Pathogenicity and virulence of malaria: Sticky problems and tricky solutions
Abstract
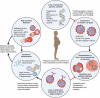
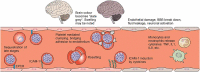
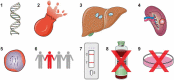
Infections with Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax cause over 600,000 deaths each year, concentrated in Africa and in young children, but much of the world's population remain at risk of infection. In this article, we review the latest developments in the immunogenicity and pathogenesis of malaria, with a particular focus on P. falciparum, the leading malaria killer. Pathogenic factors include parasite-derived toxins and variant surface antigens on infected erythrocytes that mediate sequestration in the deep vasculature. Host response to parasite toxins and to variant antigens is an important determinant of disease severity. Understanding how parasites sequester, and how antibody to variant antigens could prevent sequestration, may lead to new approaches to treat and prevent disease. Difficulties in malaria diagnosis, drug resistance, and specific challenges of treating P. vivax pose challenges to malaria elimination, but vaccines and other preventive strategies may offer improved disease control.
Keywords: Plasmodium falciparum; Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1; Plasmodium vivax; cytokine; hypnozoite; sequestration; severe malaria; var genes.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Word Malaria Report 2021. 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240040496
-
- Kojom Foko LP, Arya A, Sharma A, et al. Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of severe Plasmodium vivax malaria in India. J Infect. 2021;82(6):231–34. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Guidelines for Malaria. 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/guidelines-for-malaria - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
