Evaluation of feed utilization, immune response and disease resistance in striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage 1878) fed with a novel Aeromonas hydrophila biofilm vaccine
- PMID: 36419597
- PMCID: PMC9680056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fsirep.2022.100070
Evaluation of feed utilization, immune response and disease resistance in striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage 1878) fed with a novel Aeromonas hydrophila biofilm vaccine
Abstract
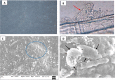
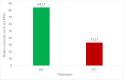
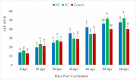
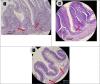
Striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus was immunized with Biofilm (BF) and Free cell (FC) of Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine at 1010 CFU g-1 for 20 days and monitored for growth parameters, immune responses and disease resistance up to 60 day post vaccination (dpv). Pangasius catfish in the BF vaccinated group had considerably higher growth and feed utilization than the FC vaccinated and unvaccinated groups (p < 0.05). Biofilm vaccinated group showed a significant increase (p < 0.05) in the mean weight gain (46.91 ± 0.59) than the FC (35.94 ± 0.21) and unvaccinated group (34.92 ± 0.35). The vaccinated fishes were challenged with A. hydrophila at 107 CFU/ml. Significant higher relative percentage survival (RPS) was recorded with BF (84.21 ± 1.49%) compared to that with FC (33.33 ± 1.21%). Polyclonal antibody-based ELISA was used to quantify the antibody titre. BF vaccinated group showed significantly higher antibody titer compared to other treatments (p < 0.05). Moreover, higher haematological parameters recorded in the present study were differentially stimulated by the oral administration of A. hydrophila biofilm vaccine. The mean total protein, albumin, and globulin levels of the BF vaccine groups were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than the mean total protein, albumin, and globulin contents of the unvaccinated group. Furthermore, biochemical stress parameters (SGPT, SGOT) in the vaccinated groups showed an incremental trend in the early days of the experimental period. However, the values were significantly lower (p < 0.05) in the biofilm group on 20 dpv onwards indicating improved health condition. Vaccinated BF fishes showed gut associated lymphoid tissues (GALT) within the laminar propria of mid gut. But in FC group fishes showed less aggregation of lymphoid cells. The unvaccinated control fish had no lymphoid cell aggregation in their intestines. The findings of the current research suggested that biofilm vaccine has the capability to be one of the potential oral vaccines in striped catfish against A. hydrophila infection.
Keywords: Biofilm based oral vaccine; Growth performance; Gut associated lymphoid tissues; Haemato-biochemical indices; Polyclonal antibody; Striped catfish.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests stated by the authors.
Figures







References
-
- FAO, Aquaculture. http://www.fao.org/fishery/aquaculture/en, 2018 (accessed on 20 Dec 2020).
-
- Ferguson W.H., Turnbull J.F., Shinn A., Thompson K., Dung T.T., Crumlish M. Bacillary necrosis in farmed Pangasius hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878) from the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. J. Fish Dis. 2001;24:509–513. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2761.2001.00308.x. - DOI
-
- Yuasa K., Edy B.K., Panigoro N., Hatai K. First isolation of Edwardsiella ictaluri from cultured striped catfish Pangasius hypophthalmus in Indonesia. Fish Pathol. 2003;38:181–183. doi: 10.3147/jsfp.38.181. - DOI
-
- Subagja J., Slembrouck J., Hung L.T., Legendre L. Larval rearing of an Asian catfish Pangasius hypophthalmus (Siluroidei Pangasiidae): analysis of precocious mortality and proposition of appropriate treatments. Aquat. Living Resour. 1999;12:37–44. doi: 10.1016/S0990-7440(99)80013-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

