Acupuncture Alleviates Corneal Inflammation in New Zealand White Rabbits with Dry Eye Diseases by Regulating α 7nAChR and NF- κ B Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36419616
- PMCID: PMC9678486
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6613144
Acupuncture Alleviates Corneal Inflammation in New Zealand White Rabbits with Dry Eye Diseases by Regulating α 7nAChR and NF- κ B Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to determine the mechanism of improvement in dry eye diseases (DEDs) treated by acupuncture. The inflammatory molecules and related pathways will be analyzed in our study.
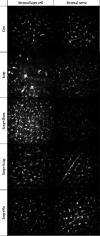
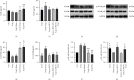
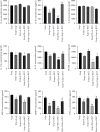
Methods: In order to establish the animal model for DEDs, healthy New Zealand white rabbits were treated with scopolamine (Scop) hydrobromide for 21 consecutive days. After 21 days, acupuncture, fluorometholone (Flu), and α7nAChR antagonist (α-BGT) treatments were performed, and the Scop injections were continued until day 35. The therapeutic effect of acupuncture on DED inflammation was evaluated by corneal fluorescence staining, tear film rupture time, tear flow measurement, in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM), corneal histopathology, and cytokine protein chip technology. The influence of acupuncture on the corneal pathology and inflammatory factors ACh, α7nAChR, and NF-κB was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and western blot.
Results: Compared with the group Scop, acupuncture can significantly reduce corneal staining and increase the tear film rupture time and tear flow, which are accompanied by a decrease in corneal epithelial detachment and lymphocyte infiltration. Acupuncture can relieve the inflammation of corneal stroma and mitigate the expression of proinflammatory factors and chemokines. Acupuncture can upregulate the expression of ACh and α7nAChR and downregulate the expression of NF-κB.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that acupuncture can alleviate corneal inflammation in New Zealand white rabbits with DEDs via α7nAChR and NF-κB signaling pathway regulation. The expression indicates that α7nAChR/NF-κB signaling pathway may be active and that acupuncture is a potential therapeutic target for dry eye.
Copyright © 2022 Ning Ding et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture Alleviates Inflammation of Dry Eye Diseases by Regulating the α7nAChR/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 9;2021:6673610. doi: 10.1155/2021/6673610. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33897942 Free PMC article.
-
[Acupuncture mitigates ocular surface inflammatory response via α7nAChR/NF-κB p65 signaling in dry eye guinea pigs].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Nov 25;47(11):975-82. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20220015. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36453674 Chinese.
-
[Effect of acupuncture on expression of transfer growth factor-β1 in lacrimal gland of rabbits with dry eye].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020 Sep 25;45(9):726-30. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190977. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020. PMID: 32959555 Chinese.
-
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Aggravate Depression-Associated Dry Eye Via Activating the NF-κB Pathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Jan 2;60(1):407-419. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-25572. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30695093
-
The Role of α7nAChR-Mediated Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway in Immune Cells.Inflammation. 2021 Jun;44(3):821-834. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01396-6. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33405021 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Acupuncture for the Treatment of Dry Eye Syndrome: Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Clinical Implications.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Aug 22;18:4647-4658. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S526265. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40874238 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones L., Downie L. E., Korb D., et al. TFOS DEWS II management and therapy report. Ocular Surface . 2017;15(3):575–628. - PubMed
-
- Podolsky D. K. Inflammatory bowel disease. New England Journal of Medicine . 2002;347(6):417–429. - PubMed
-
- Song X. J., Li D. Q., Farley W., et al. Neurturin-deficient mice develop dry eye and keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science . 2003;44(10):4223–4229. - PubMed
-
- Tracey K. J. The inflammatory reflex. Nature . 2002;420(6917):853–859. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

