Genetic analysis and prenatal diagnosis of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa caused by compound heterozygous variants of the COL7A1 gene in a Chinese family
- PMID: 36419915
- PMCID: PMC9676484
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.941201
Genetic analysis and prenatal diagnosis of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa caused by compound heterozygous variants of the COL7A1 gene in a Chinese family
Abstract
Background: Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is an incurable and inherited skin disorder mainly caused by mutations in the gene encoding type VII collagen (COL7A1). The purpose of this study was to identify the causative genetic variants and further perform genetic diagnosis in a Chinese family affected by DEB.
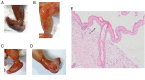
Methods: High-throughput sequencing was performed to analyze the genetic skin disorder-related genes of parents of the proband, and the variants were further confirmed in the other members by Sanger sequencing. Sanger sequencing, karyotype analysis, and chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) were used together for prenatal diagnosis after the second pregnancy. The phenotype of the fetus was tracked after the diagnosis and induction of labor. Moreover, skin and muscle pathological examination and whole-exome sequencing (WES) of the skin and muscle tissue of the induced fetus were performed.
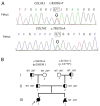
Results: Here, we determined two heterozygous variants of the COL7A1 gene that contributed to the autosomal recessive DEB (RDEB) in the family, i.e., a novel pathogenic variant (c.8335G > T, p.E2779*) and a likely pathogenic variant (c.7957G > A, p.G2653R). Sanger sequencing of amniotic fluid cells showed that the fetus carried the above two compound heterozygous variants, and the karyotype analysis and CMA results showed no abnormality. The clinical phenotype and pathological results of the induced fetus were consistent with the characteristics of DEB. Further, WES analysis also confirmed a novel compound heterozygous variation in COL7A1, consisting of two variants, namely, c.8335G > T and c.7957G > A in the fetus.
Conclusion: This study expands the spectrum of disease-causing variants of COL7A1 and provides a theoretical basis for diagnosis, genetic counseling, and prognosis of families affected by RDEB.
Keywords: COL7A1; autosomal recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa; compound heterozygous variants; high-throughput sequencing analysis; prenatal diagnosis.
© 2022 Wang, Song, Zhang, Li, Zhao, Yang, Ji and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
SJ was employed by Yinfeng Gene Technology Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Novel Biallelic Causative Variants in COL7A1 Gene by Whole-Exome Sequencing, Resulting in Congenital Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa in Three Unrelated Families.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jun 23;12(7):1525. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12071525. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885431 Free PMC article.
-
A homozygous nonsense mutation identified in COL7A1 in a family with autosomal recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.J Med Life. 2024 Sep;17(9):892-896. doi: 10.25122/jml-2024-0090. J Med Life. 2024. PMID: 39628969 Free PMC article.
-
Novel and very rare causative variants in the COL7A1 gene of Vietnamese patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa revealed by whole-exome sequencing.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Aug;9(8):e1748. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1748. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 34286919 Free PMC article.
-
Review of collagen VII sequence variants found in Australasian patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa reveals nine novel COL7A1 variants.J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Jun;46(3):169-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.02.006. Epub 2007 Apr 10. J Dermatol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17425959 Review.
-
Mutation analysis and characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.Exp Dermatol. 2008 Jul;17(7):553-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00723.x. Exp Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18558993 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidermolysis Bullosa: Two rare case reports of COL7A1 and EBS-GEN SEV KRT14 variants with review of literature.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Apr 5;24(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04715-0. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38580989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic diagnosis of a rare COL7A1 variant causing dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa through whole‑exome sequencing.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Sep 11;26(5):502. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12201. eCollection 2023 Nov. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37822584 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

