Intrathecal immunoglobin synthesis and its role in patients with neurosyphilis
- PMID: 36419997
- PMCID: PMC9677103
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1008595
Intrathecal immunoglobin synthesis and its role in patients with neurosyphilis
Abstract
Background: Intrathecal protein synthesis (ITS) occurs in various central nervous system disorders, but few quantitative studies have focused on ITS for neurosyphilis (NS) in southwestern China. We made a study to quantitatively assess the ITS in patients with NS and to investigate the association between ITS and the stages of NS.
Methods: CSF-serum specimen pairs from 142 patients (66 NS and 76 non-NS/syphilis) were collected for routine CSF and serum tests. The NS group was divided into slight and severe subgroups according to the NS stages. Three formulas for the quantitative determination of the intrathecal synthesis were calculated to characterize the specimens, including the Ig index (QIg/Qalb), Ig extended index (Ig_EI), and intrathecally synthesized fraction (IgIF) using the hyperbolic function. The role of QTPPA/QIgG as an antibody index (AI = Q specific Ig/QIgG) was also explored.
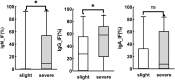
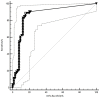
Results: Sero_TRUST titres (1:16, 1:1-1:256), sero_TPPA titres (1:163840, 1:1280-1:1310720), total protein (MTP), and CSF_Igs (p < 0.05) were found to be significantly elevated in the NS group. Intrathecal Ig synthesis can be identified using all three formulas in the NS group. The pattern of Ig intrathecal synthesis was IgIF-G (48.62%) > IgIF-A = IgIF-M (p < 0.05), with the dominant intrathecal fraction being IgG (median, 48.62%), which was also verified by QIgG> Qalb> QIgM = QIgA. In the slight NS group, the intrathecal fractions of IgM (>0 in 4 out of 20 cases) and IgG (>0 in 16 out of 20) were lower than the intrathecal fractions of IgM (>0 in 19 out of 35 cases) and IgG (>0 in 33 out of 38) in the severe group (p < 0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) of the CSF_TPPA antibody index was 0.867 (0.792, 0.922), with an optimal cutoff point of 0.81, providing a sensitivity of 88.91% and specificity of 84.62%.
Conclusion: Although the intrathecal synthesis pattern is IgG dominant in patients with NS, brain-derived IgM and IgA can also be found. Moreover, intrathecal IgM and IgG were associated with a parenchymatous type of neurosyphilis. Syphilis-specific antibodies are a new potential tool for NS diagnosis.
Keywords: central nervous system; cerebrospinal fluid; immunoglobulins; intrathecal synthesis; neurosyphilis.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Ying, Luo, Li, Li and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intrathecal Synthesis Index of Specific Anti-Treponema IgG: a New Tool for the Diagnosis of Neurosyphilis.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0147721. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01477-21. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35138118 Free PMC article.
-
Multicentric evaluation of a specific intrathecal anti-Treponema pallidum IgG index as a diagnostic biomarker of neurosyphilis: results from a retro-prospective case-control study.Sex Transm Infect. 2024 Feb 19;100(2):63-69. doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2023-055913. Sex Transm Infect. 2024. PMID: 38071543
-
Criteria for the diagnosis of neurosyphilis in cerebrospinal fluid: relationships with intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier dysfunction.Sex Transm Dis. 2013 Dec;40(12):917-22. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000049. Sex Transm Dis. 2013. PMID: 24220351
-
Intrathecal IgA synthesis in neurosyphilis.J Neurol Sci. 2005 Jan 15;228(1):21-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2004.09.028. J Neurol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15607206
-
A modern approach to CSF analysis: pathophysiology, clinical application, proof of concept and laboratory reporting.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009 May;111(4):313-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2008.12.004. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009. PMID: 19185983 Review.
Cited by
-
The application value of cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin in tuberculous meningitis.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0015724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00157-24. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38666897 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and laboratory characteristics of neurosyphilis: analysis of symptoms and risk factors.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 26;30(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02349-1. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40011955 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

