Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and metabolic goal achievement with risk of chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 36420005
- PMCID: PMC9676964
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1047794
Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and metabolic goal achievement with risk of chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Although type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) plays a significant role in the association between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), how T2DM development and glycemic deterioration affect CKD and its renal function indicators, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), remains unknown. We aimed to assess the association between MAFLD, along with T2DM, and risk of CKD, and then evaluate the effect of metabolic goal achievement in MAFLD on the risk of CKD.
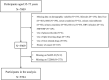
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 5,594 participants were included. Multivariate logistic regression and linear regression were used to examine the association between MAFLD with its T2DM status and metabolic goal achievement and risk of CKD, as well as eGFR and UACR.
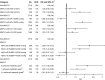
Results: The MAFLD group had a higher prevalence of CKD (16.2 vs. 7.6%, P < 0.001) than the non-MAFLD group. MAFLD was independently associated with an increased risk of CKD (odds ratio [OR]: 1.35, 95% CI: 1.09-1.67) and increased eGFR and UACR. Among the three MAFLD subtypes, only the T2DM subtype exhibited significant associations with increased risk of CKD (OR: 2.85, 95% CI: 2.24-3.63), as well as increased eGFR and UACR. Glycemic deterioration in MAFLD was dose-dependently associated with an increased risk of CKD (P-trend < 0.001). Achieved metabolic goals in MAFLD decreased the risk of CKD, eGFR, and UACR; MAFLD with 2 or 3 achieved metabolic goals was not significantly associated with the risk of CKD (OR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.59-1.12) and albuminuria.
Conclusion: MAFLD was independently associated with an increased risk of CKD, as well as increased eGFR and UACR. This association is strongly driven by T2DM status. Glycemic deterioration in MAFLD was dose-dependently associated with an increased risk of CKD. Achieved metabolic goals in MAFLD decreased the risk of CKD by reducing the risk of albuminuria.
Keywords: albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; estimated glomerular filtration rate; metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; metabolic goal achievement; type 2 diabetes mellitus; urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio.
Copyright © 2022 Su, Chen, Xiao, Du, Xue, Feng and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

