Effects of Photon Radiation on DNA Damage, Cell Proliferation, Cell Survival, and Apoptosis of Murine and Human Mesothelioma Cell Lines
- PMID: 36420194
- PMCID: PMC9677206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2022.101013
Effects of Photon Radiation on DNA Damage, Cell Proliferation, Cell Survival, and Apoptosis of Murine and Human Mesothelioma Cell Lines
Abstract
Purpose: To characterize the cellular responses of murine and human mesothelioma cell lines to different doses of photon radiation with a long-term aim of optimizing a clinically relevant in vivo model in which to study the interaction of radiation therapy and immunotherapy combinations.
Methods and materials: Two murine mesothelioma cell lines (AB1 and AE17) and 3 human cell lines (BYE, MC, and JU) were used in the study. Cells were treated with increasing doses of photon radiation. DNA damage, DNA repair, cell proliferation, and apoptosis at different time points after irradiation were quantified by flow cytometry, and cell survival probability was examined using clonogenic survival assay.
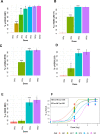
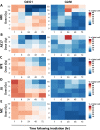
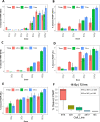
Results: DNA damage increased with escalating dose in all cell lines. Evident G2/M arrest and reduced cell proliferation were observed after irradiation with 8 Gy. DNA repair was uniformly less efficient at higher compared with lower radiation-fraction doses. The apoptosis dose response varied between cell lines, with greater apoptosis observed at 16 Gy with human BYE and murine AB1 cell lines but less for other studied cell lines, regardless of dose and time. The α/β ratio from the cell survival fraction of human mesothelioma cell lines was smaller than from murine ones, suggesting human cell lines in our study were more sensitive to a change of dose per fraction than were murine mesothelioma cell lines. However, in all studied cell lines, colony formation was completely inhibited at 8 Gy.
Conclusions: A threshold dose of 8 Gy appeared to be appropriate for hypofractionated radiation therapy. However, the radiation therapy doses between 4 and 8 Gy remain to be systematically analyzed. These observations provide an accurate picture of the in vitro response of mesothelioma cell lines to photon irradiation and characterize the heterogeneity between human and murine cell lines. This information may guide in vivo experiments and the strengths and limitations of extrapolation from murine experimentation to potential human translation.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immune marker expression of irradiated mesothelioma cell lines.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 31;12:1020493. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1020493. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387076 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitivity, apoptosis and repair of DNA double-strand breaks in radiation-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants treated at different dose rates.Radiat Res. 1996 Dec;146(6):636-45. Radiat Res. 1996. PMID: 8955713
-
In vitro effects of radiation on human retinoblastoma cells.Int J Cancer. 2001;96 Suppl:7-14. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10344. Int J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11992382
-
Patterns of failure following surgical resection for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Thorac Surg Clin. 2004 Nov;14(4):567-73. doi: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2004.06.006. Thorac Surg Clin. 2004. PMID: 15559064 Review.
-
Overview of radiosensitivity of human tumor cells to low-dose-rate irradiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008 Nov 1;72(3):909-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1928. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. PMID: 19014780 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphological aspects of small intestinal mucosal injury and repair after electron irradiation.Anat Cell Biol. 2024 Sep 30;57(3):384-391. doi: 10.5115/acb.24.050. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Anat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38880781 Free PMC article.
-
Immune marker expression of irradiated mesothelioma cell lines.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 31;12:1020493. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1020493. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387076 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic in silico explorations of the immunogenic and synergistic effects of radiotherapy and immunotherapy: a critical review.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024 Dec;47(4):1291-1306. doi: 10.1007/s13246-024-01458-1. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 39017990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J, et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2636–2644. - PubMed
-
- Baas P, Scherpereel A, Nowak AK, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:375–386. - PubMed
-
- Zalcman G, Mazieres J, Margery J, et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1405–1414. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

