Sustainable recovery of MBNL activity in autoregulatory feedback loop in myotonic dystrophy
- PMID: 36420218
- PMCID: PMC9672890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.10.023
Sustainable recovery of MBNL activity in autoregulatory feedback loop in myotonic dystrophy
Abstract
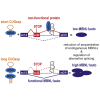
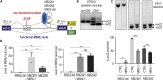
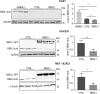
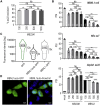
Muscleblind-like proteins (MBNLs) are RNA-binding proteins essential for the developmental regulation of various processes including alternative splicing. Their activity is misregulated in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), an incurable genetic, neuro-muscular disorder caused by uncontrolled expansion of CTG repeats. Mutant RNAs containing hundreds or thousands of repeats efficiently sequester MBNL proteins. As a consequence, global alternative splicing abnormalities are induced. Importantly, the size of expansion differs significantly not only between patients but also between different parts of the same muscle as a consequence of somatic expansion. One of the potential therapeutic strategies in DM is overexpression of MBNLs. However, gene therapy tools might induce excessive activity of MBNLs, what in turn might change the metabolism of many RNAs. To overcome these limitations, we designed an autoregulated MBNL1 overexpression system. The genetic construct contains an MBNL1-coding sequence separated by the fragment of ATP2A1 pre-mRNA with an MBNL-sensitive alternative exon containing stop codon in the reading frame of MBNL1. Inclusion of this exon leads to the arrangement of an inactive form of the protein, but exclusion gives rise to fully active MBNL1. This approach enables the autoregulation of the amount of overexpressed MBNL1 with high dynamic range which ensures a homogeneous level of this protein in cells treated with the genetic construct. We demonstrated beneficial effects of an autoregulated construct on alternative splicing patterns in DM1 models and cells derived from patients with DM1.
Keywords: DM1; MBNL; MBNL1 overexpression; MT: Delivery Strategies; alternative splicing; expansion of CCUG repeats; expansion of CUG repeats; gene therapy; microsatellites; myotonic dystrophy type 1.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tau exon 2 responsive elements deregulated in myotonic dystrophy type I are proximal to exon 2 and synergistically regulated by MBNL1 and MBNL2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Apr;1842(4):654-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24440524
-
MBNL expression in autoregulatory feedback loops.RNA Biol. 2018 Jan 2;15(1):1-8. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1384119. Epub 2017 Nov 13. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 28949831 Free PMC article.
-
MBNL splicing factors regulate the microtranscriptome of skeletal muscles.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 28;52(19):12055-12073. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae774. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39258536 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecules Which Improve Pathogenesis of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1.Front Neurol. 2018 May 18;9:349. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00349. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29867749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hallmarks of myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle dysfunction.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2021 Apr;96(2):716-730. doi: 10.1111/brv.12674. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2021. PMID: 33269537 Review.
Cited by
-
Multisystem Symptoms in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1: A Management and Therapeutic Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 2;26(11):5350. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115350. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of the Muscleblind-like protein family and their role in disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 18;23(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02102-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39966885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying new players in structural synaptic plasticity through dArc1 interrogation.iScience. 2023 Sep 27;26(11):108048. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108048. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37876812 Free PMC article.
-
Altered drug metabolism and increased susceptibility to fatty liver disease in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 21;15(1):9062. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53378-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39433769 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter-targeted small RNA duplexes increase MBNL1 transcription and mitigate myotonic dystrophy-associated spliceopathy.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Aug 11;53(15):gkaf756. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf756. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40829807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang E.T., Cody N.A.L., Jog S., Biancolella M., Wang T.T., Treacy D.J., Luo S., Schroth G.P., Housman D.E., Reddy S., et al. Transcriptome-wide regulation of pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA localization by muscleblind proteins. Cell. 2012;150:710–724. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.041. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

