Interobserver agreement and procedural fidelity: An odd asymmetry
- PMID: 36420837
- PMCID: PMC10098472
- DOI: 10.1002/jaba.961
Interobserver agreement and procedural fidelity: An odd asymmetry
Abstract
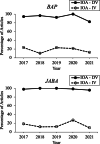
We examined articles with experiments published in the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis and in Behavior Analysis in Practice from 2017 through 2021 to determine how frequently procedural fidelity was assessed. When procedural fidelity was assessed, we determined how often a measure of interobserver agreement for those fidelity data was provided. We also determined how often a measure of interobserver agreement for participants' behavior was provided. Across both journals and all years, 54.7% of relevant articles provided a measure of procedural fidelity. Of them, 17.7% provided a measure of interobserver agreement for procedural fidelity. In marked contrast, 96.4% provided interobserver agreement data for participants' behavior. It is unfortunate that applied behavior analysts frequently fail to provide procedural fidelity data and, when they do, often fail to provide interobserver agreement data for the fidelity data. Reviewers for, and editors of, behavior-analytic journals are encouraged to strongly consider the relative value of procedural fidelity and agreement on procedural fidelity measures when rendering recommendations on the suitability of a given submission.
Keywords: human observers; interobserver agreement; procedural fidelity; treatment integrity.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Society for the Experimental Analysis of Behavior (SEAB).
Figures

References
-
- Andzik, N. R. , Cannella‐Malone, H. I. , & Sigafoos, J. (2016). Practitioner implementer functional communication training: A literature review. Research and Practice for Persons with Severe Disabilities, 41(2), 79–89. 10.1177/1540796916633874 - DOI
-
- Cooper, J. O. , Heron, T. E. , & Heward, W. L. (2020). Applied behavior analysis (3rd ed.). Pearson.
-
- DiGennaro Reed, F. D. , & Codding, R. S. (2014). Advancements in procedural fidelity assessment and intervention: Introduction to the special issue. Journal of Behavioral Education, 23(1), 1–18. 10.1007/s10864-013-9191-3 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

