Evaluation of 10-minute post-injection 11C-PiB PET and its correlation with 18F-FDG PET in older adults who are cognitively healthy, mildly impaired, or with probable Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36420910
- PMCID: PMC9561831
- DOI: 10.47626/1516-4446-2021-2374
Evaluation of 10-minute post-injection 11C-PiB PET and its correlation with 18F-FDG PET in older adults who are cognitively healthy, mildly impaired, or with probable Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Objective: Positron emission tomography (PET) allows in vivo evaluation of molecular targets in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease. Mild cognitive impairment is an intermediate stage between normal cognition and Alzheimer-type dementia. In vivo fibrillar amyloid-beta can be detected in PET using [11C]-labeled Pittsburgh compound B (11C-PiB). In contrast, [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose (18F-FDG) is a neurodegeneration biomarker used to evaluate cerebral glucose metabolism, indicating neuronal injury and synaptic dysfunction. In addition, early cerebral uptake of amyloid-PET tracers can determine regional cerebral blood flow. The present study compared early-phase 11C-PiB and 18F-FDG in older adults without cognitive impairment, amnestic mild cognitive impairment, and clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer's disease.
Methods: We selected 90 older adults, clinically classified as healthy controls, with amnestic mild cognitive impairment, or with probable Alzheimer's disease, who underwent an 18F-FDG PET, early-phase 11C-PiB PET and magnetic resonance imaging. All participants were also classified as amyloid-positive or -negative in late-phase 11C-PiB. The data were analyzed using statistical parametric mapping.
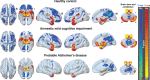
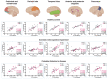
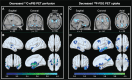
Results: We found that the probable Alzheimer's disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment group had lower early-phase 11C-PiB uptake in limbic structures than 18F-FDG uptake. The images showed significant interactions between amyloid-beta status (negative or positive). However, early-phase 11C-PiB appears to provide different information from 18F-FDG about neurodegeneration.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that early-phase 11C-PiB uptake correlates with 18F-FDG, irrespective of the particular amyloid-beta status. In addition, we observed distinct regional distribution patterns between both biomarkers, reinforcing the need for more robust studies to investigate the real clinical value of early-phase amyloid-PET imaging.
Keywords: Positron emission tomography; [11C]-labeled Pittsburgh compound B; [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose; aging; amyloid; cerebral glucose metabolism; neuroimaging; perfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Cross-Validation of FDG- and Amyloid-PET Biomarkers in Mild Cognitive Impairment for the Risk Prediction to Dementia due to Alzheimer's Disease in a Clinical Setting.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;59(2):603-614. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170158. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28671117
-
Biopathological Significance of Early-Phase Amyloid Imaging in the Spectrum of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;69(2):529-538. doi: 10.3233/JAD-181188. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31104023
-
Can 11C-PiB-PET Relative Delivery R1 or 11C-PiB-PET Perfusion Replace 18F-FDG-PET in the Assessment of Brain Neurodegeneration?J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;65(1):89-97. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180274. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 30056421 Free PMC article.
-
Early detection of Alzheimer's disease using PiB and FDG PET.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Dec;72 Pt A:117-22. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 May 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24825318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular neuroimaging in degenerative dementias.Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2013 Sep-Oct;32(5):301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.remn.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2013. PMID: 23933381 Review. English, Spanish.
Cited by
-
Advancements in dementia research, diagnostics, and care in Latin America: Highlights from the 2023 Alzheimer's Association International conference satellite symposium in Mexico City.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Jul;20(7):5009-5026. doi: 10.1002/alz.13850. Epub 2024 May 27. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38801124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicity Concerns Associated with the Radiopharmaceuticals for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(2):83-86. doi: 10.2174/0118715249340822240828065449. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39248065 No abstract available.
-
Biomarkers of neurodegeneration across the Global South.Lancet Healthy Longev. 2024 Oct;5(10):100616. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(24)00132-6. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2024. PMID: 39369726 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer’s disease. New Engl J Med. 2010;362:329–44. - PubMed
-
- Petersen RC, Doody R, Kurz A, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rabins PV, et al. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:1985–92. - PubMed
-
- Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E. Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol. 1999;56:303–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
