Automated Lung-Related Pneumonia and COVID-19 Detection Based on Novel Feature Extraction Framework and Vision Transformer Approaches Using Chest X-ray Images
- PMID: 36421110
- PMCID: PMC9687434
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9110709
Automated Lung-Related Pneumonia and COVID-19 Detection Based on Novel Feature Extraction Framework and Vision Transformer Approaches Using Chest X-ray Images
Abstract
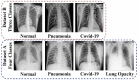
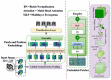
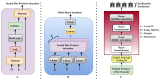
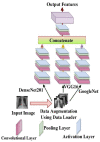
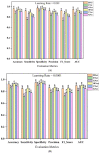
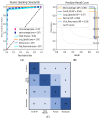
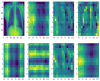
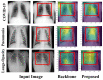
According to research, classifiers and detectors are less accurate when images are blurry, have low contrast, or have other flaws which raise questions about the machine learning model's ability to recognize items effectively. The chest X-ray image has proven to be the preferred image modality for medical imaging as it contains more information about a patient. Its interpretation is quite difficult, nevertheless. The goal of this research is to construct a reliable deep-learning model capable of producing high classification accuracy on chest x-ray images for lung diseases. To enable a thorough study of the chest X-ray image, the suggested framework first derived richer features using an ensemble technique, then a global second-order pooling is applied to further derive higher global features of the images. Furthermore, the images are then separated into patches and position embedding before analyzing the patches individually via a vision transformer approach. The proposed model yielded 96.01% sensitivity, 96.20% precision, and 98.00% accuracy for the COVID-19 Radiography Dataset while achieving 97.84% accuracy, 96.76% sensitivity and 96.80% precision, for the Covid-ChestX-ray-15k dataset. The experimental findings reveal that the presented models outperform traditional deep learning models and other state-of-the-art approaches provided in the literature.
Keywords: COVID-19; artificial intelligence; automatic detection; chest X-rays images; epidemic; feature extraction; lung disease; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fong S.J., Dey N., Chaki J. SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology. Springer; Singapore: 2021. An Introduction to COVID-19; pp. 1–22.
-
- Bentivegna E., Luciani M., Spuntarelli V., Speranza M.L., Guerritore L., Sentimentale A., Martelletti P. Extremely Severe Case of COVID-19 Pneumonia Recovered Despite Bad Prognostic Indicators: A Didactic Report. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020;2:1204–1207. doi: 10.1007/s42399-020-00383-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

