A Review on Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Biosensors of Glucose Using Carbon Nanofiber Nanocomposites
- PMID: 36421123
- PMCID: PMC9688744
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12111004
A Review on Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Biosensors of Glucose Using Carbon Nanofiber Nanocomposites
Abstract
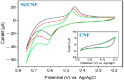
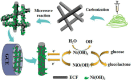
Diabetes mellitus has become a worldwide epidemic, and it is expected to become the seventh leading cause of death by 2030. In response to the increasing number of diabetes patients worldwide, glucose biosensors with high sensitivity and selectivity have been developed for rapid detection. The selectivity, high sensitivity, simplicity, and quick response of electrochemical biosensors have made them a popular choice in recent years. This review summarizes the recent developments in electrodes for non-enzymatic glucose detection using carbon nanofiber (CNF)-based nanocomposites. The electrochemical performance and limitations of enzymatic and non-enzymatic glucose biosensors are reviewed. Then, the recent developments in non-enzymatic glucose biosensors using CNF composites are discussed. The final section of the review provides a summary of the challenges and perspectives, for progress in non-enzymatic glucose biosensors.
Keywords: carbon nanofiber; electrochemical biosensors; electrodes; nanocomposite; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrochemical biosensors based on polymer nanocomposites for detecting breast cancer: Recent progress and future prospects.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Nov;309:102795. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2022.102795. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 36242876 Review.
-
An Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Aptasensor for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2-RBD Using a Carbon Nanofiber-Gold Nanocomposite Modified Screen-Printed Electrode.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;12(3):142. doi: 10.3390/bios12030142. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35323412 Free PMC article.
-
A review on recent advancements in electrochemical biosensing using carbonaceous nanomaterials.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Nov 13;186(12):773. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3854-2. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31720840 Review.
-
Biosensors-Recent Advances and Future Challenges in Electrode Materials.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jun 23;20(12):3561. doi: 10.3390/s20123561. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32586032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesoporous polyaniline nanofiber decorated graphene micro-flowers for enzyme-less cholesterol biosensors.Nanotechnology. 2016 Aug 26;27(34):345101. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/27/34/345101. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Nanotechnology. 2016. PMID: 27419910
Cited by
-
Multilayer Core-Sheath Structured Nickel Wire/Copper Oxide/Cobalt Oxide Composite for Highly Sensitive Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;15(6):411. doi: 10.3390/nano15060411. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137584 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Fe-Doped Peroxidase Mimetic Nanozymes from Natural Hemoglobin for Colorimetric Biosensing and In Vitro Anticancer Effects.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 May 27;13(6):583. doi: 10.3390/bios13060583. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366948 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Glucose Sensors.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Apr 20;8(2):167. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8020167. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37092419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functionalization of Carbon Nanofibers with an Aromatic Diamine: Toward a Simple Electrochemical-Based Sensing Platform for the Selective Sensing of Glucose.ACS Omega. 2024 Jun 11;9(25):27085-27092. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00525. eCollection 2024 Jun 25. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38947806 Free PMC article.
-
Acetate-assisted in situ electrodeposited β-MnO2 for the fabrication of nano-architectonics for non-enzymatic glucose detection.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 15;14(31):22359-22367. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03930k. eCollection 2024 Jul 12. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39010910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bamgboje D., Christoulakis I., Smanis I., Chavan G., Shah R., Malekzadeh M., Violaris I., Giannakeas N., Tsipouras M., Kalafatakis K., et al. Continuous Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring via Contact Lenses: Current Approaches and Future Perspectives. Biosensors. 2021;11:189. doi: 10.3390/bios11060189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cano Perez J.L., Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez J., Perezcampos Mayoral C., Pérez-Campos E.L., Pina Canseco M.d.S., Tepech Carrillo L., Mayoral L.P.-C., Vargas Treviño M., Apreza E.L., Rojas Laguna R. Fiber Optic Sensors: A Review for Glucose Measurement. Biosensors. 2021;11:61. doi: 10.3390/bios11030061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed J., Rashed M.A., Faisal M., Harraz F.A., Jalalah M., Alsareii S.A. Novel SWCNTs-Mesoporous Silicon Nanocomposite as Efficient Non-Enzymatic Glucose Biosensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021;552:149477. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149477. - DOI
-
- WHO . Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

