Electrochemical Immunosensor for Early Detection of β-Amyloid Alzheimer's Disease Biomarker Based on Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Gold Nanocomposites
- PMID: 36421177
- PMCID: PMC9688776
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12111059
Electrochemical Immunosensor for Early Detection of β-Amyloid Alzheimer's Disease Biomarker Based on Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Gold Nanocomposites
Abstract
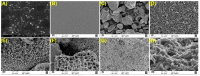
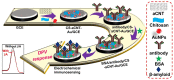
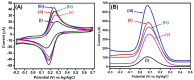
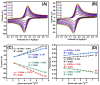
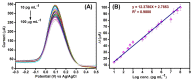
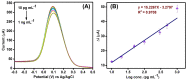
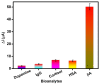
Beta-amyloid (βA) peptides accompanying the physiological change in brain induce Alzheimer's disease. In this work, a highly sensitive electrochemical (EC) immunosensor platform has been developed for the quantitative detection of βA peptides, using the gold nanoparticle functionalized chitosan-aligned carbon nanotube (CS-aCNT-Au) nanocomposites on glassy carbon electrodes (GCE). The immunosensor has been fabricated by immobilization of the anti-βA antibody upon CS-aCNT-Au/GCE. In the CS-aCNT nanocomposite, CS has high biocompatibility. Hydroxy and amine functionalities favor the antibody immobilization and prevent the leaching of nanocomposites of the modified electrode due to the adhesive environment. Moreover, aCNT offers high conductivity, stability, and a large surface area (the calculated effective surface area of the CS-aCNT/GCE is 8.594 × 10-2 cm2). However, the incorporation of AuNPs further enhances the conductivity of the CS-aCNT-Au nanocomposite based on differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) results, and also improves the effective surface area (9.735 × 10-2 cm2). The surface morphology and electrochemical studies of the nanocomposite, as well as its modifications by the anti-βA antibody and BSA, were carried out through field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and DPV. The quantitative immunosensing of the βA in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution is accomplished via DPV, which reveals that the immunosensor has a high sensitivity of 157.60 µA pg-1 mL cm-2 and a broad detection range of 10.0 pg mL-1-100.0 µg mL-1, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.87 pg mL-1. Subsequently, we detected the spiked βA in diluted serum with a linear detection range of 10.0 pg mL-1-1.0 ng mL-1 and LOD of 0.95 pg mL-1. Moreover, a selectivity study exhibited a high affinity of immunosensors towards βA. Thus, we propose that this highly efficient immunosensor can potentially be applied for the point-of-care (POC) sensing of βA in clinical samples.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; aligned carbon nanotube; chitosan; electrochemical immunosensor; gold nanoparticles; β-amyloid peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict to declare by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Au/NiFe2O4 nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide nanosheets for electrochemical immunosensing of amyloid beta peptide.Nanoscale Adv. 2019 Nov 5;2(1):239-248. doi: 10.1039/c9na00578a. eCollection 2020 Jan 22. Nanoscale Adv. 2019. PMID: 36133989 Free PMC article.
-
A disposable electrochemical immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on nano-Au/multi-walled carbon nanotubes-chitosans nanocomposite film modified glassy carbon electrode.Anal Chim Acta. 2010 Feb 5;659(1-2):102-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.11.023. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Anal Chim Acta. 2010. PMID: 20103110
-
Bio-nanocomposite based highly sensitive and label-free electrochemical immunosensor for endometriosis diagnostics application.Bioelectrochemistry. 2021 Jun;139:107740. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2021.107740. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Bioelectrochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33524653
-
Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor system for determination of autologous SOX2 antibody.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024 Apr 15;241:115992. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.115992. Epub 2024 Jan 20. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024. PMID: 38277708 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Electrochemical Immunosensors with Nanomaterial Assistance for Signal Amplification.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;13(1):125. doi: 10.3390/bios13010125. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing the Early Detection of Alzheimer's Disease through Non-Invasive Biomarkers: The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 22;23(9):4184. doi: 10.3390/s23094184. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37177386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-Bioactivity Relationship of the Functionalized Polysulfone with Triethylphosphonium Pendant Groups: Perspective for Biomedical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;15(4):877. doi: 10.3390/polym15040877. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36850167 Free PMC article.
-
A reagent-free, fouling-resistant electrochemical multifunctional peptide sensor for highly sensitive and rapid detection of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 12;33:102081. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102081. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40697322 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors for Neurodegenerative Disease Biomarkers.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 28;15(3):151. doi: 10.3390/bios15030151. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SAM-Support-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Aβ Biomarker Detection of Alzheimer's Disease.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;13(8):809. doi: 10.3390/bios13080809. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Organization WHO Dementia. [(accessed on 4 October 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia#:~:text=Alzhei....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

