Reference Genes for Expression Analysis Using RT-qPCR in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)
- PMID: 36421949
- PMCID: PMC9697642
- DOI: 10.3390/insects13111046
Reference Genes for Expression Analysis Using RT-qPCR in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)
Abstract
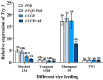
Cnaphalocrocis medinalis is a destructive migratory rice pest. Although many studies have investigated its behavioral and physiological responses to environmental changes and migration-inducing factors, little is known about its molecular mechanisms. This study was conducted to select suitable RT-qPCR reference genes to facilitate future gene expression studies. Here, thirteen candidate housekeeping genes (EF1α, AK, EF1β, GAPDH, PGK, RPL13, RPL18, RPS3, 18S rRNA, TBP1, TBP2, ACT, and UCCR) were selected to evaluate their stabilities under different conditions using the ∆CT method; the geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper algorithms; and the online tool RefFinder. The results showed that the most stable reference genes were EF1β, PGK, and RPL18, related to developmental stages; RPS3 and RPL18 in larval tissues; EF1β and PGK in larvae feeding on different rice varieties; EF1α, EF1β, and PGK in larvae temperature treatments; PGK and RPL13, related to different adult ages; PGK, EF1α, and ACT, related to adult nutritional conditions; RPL18 and PGK, related to adult mating status; and, RPS3 and PGK, related to different adult take-off characteristics. Our results reveal reference genes that apply to various experimental conditions and will greatly improve the reliability of RT-qPCR analysis for the further study of gene function in this pest.
Keywords: Cnaphalocrocis medinalis; RT-qPCR; expression stability; migratory insect; reference genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and Validation of Reference Genes for Expression Analysis Using RT-qPCR in Leptocybe invasa Fisher and La Salle (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae).Insects. 2023 May 12;14(5):456. doi: 10.3390/insects14050456. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37233084 Free PMC article.
-
Selection and Validation of Reference Genes for Gene Expression Analysis in Tuta absoluta Meyrick (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae).Insects. 2021 Jun 29;12(7):589. doi: 10.3390/insects12070589. Insects. 2021. PMID: 34209609 Free PMC article.
-
Selection and Validation of Reference Genes for Reverse-Transcription Quantitative PCR Analysis in Sclerotium rolfsii.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 15;24(20):15198. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015198. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894879 Free PMC article.
-
Reference Genes for Expression Analyses by qRT-PCR in Phthorimaea operculella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae).Insects. 2022 Jan 28;13(2):140. doi: 10.3390/insects13020140. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35206714 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of reference genes for quantitative expression analysis in Mylabris sibirica (Coleoptera, Meloidae).Front Physiol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1345836. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1345836. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38651047 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis in the Bean Bug, Riptortus pedestris (Hemiptera: Alydidae).Insects. 2023 Dec 18;14(12):960. doi: 10.3390/insects14120960. Insects. 2023. PMID: 38132633 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Reference Genes for Expression Analysis Using RT-qPCR in Leptocybe invasa Fisher and La Salle (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae).Insects. 2023 May 12;14(5):456. doi: 10.3390/insects14050456. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37233084 Free PMC article.
-
Defense Responses of Different Rice Varieties Affect Growth Performance and Food Utilization of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Larvae.Rice (N Y). 2024 Jan 20;17(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12284-024-00683-2. Rice (N Y). 2024. PMID: 38244131 Free PMC article.
-
CRY1 is involved in the take-off behaviour of migratory Cnaphalocrocis medinalis individuals.BMC Biol. 2024 Aug 13;22(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01964-4. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39135045 Free PMC article.
-
Validation and Evaluation of Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis in Mythimna loreyi (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).Insects. 2024 Mar 10;15(3):185. doi: 10.3390/insects15030185. Insects. 2024. PMID: 38535380 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

