The Role of Sfp1 in Candida albicans Cell Wall Maintenance
- PMID: 36422017
- PMCID: PMC9692975
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8111196
The Role of Sfp1 in Candida albicans Cell Wall Maintenance
Abstract
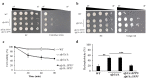
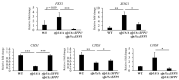
The cell wall is the first interface for Candida albicans interaction with the surrounding environment and the host cells. Therefore, maintenance of cell wall integrity (CWI) is crucial for C. albicans survival and host-pathogen interaction. In response to environmental stresses, C. albicans undergoes cell wall remodeling controlled by multiple signaling pathways and transcription regulators. Here, we explored the role of the transcription factor Sfp1 in CWI. A deletion of the SFP1 gene not only caused changes in cell wall properties, cell wall composition and structure but also modulated expression of cell wall biosynthesis and remodeling genes. In addition, Cas5 is a known transcription regulator for C. albicans CWI and cell wall stress response. Interestingly, our results indicated that Sfp1 negatively controls the CAS5 gene expression by binding to its promoter element. Together, this study provides new insights into the regulation of C. albicans CWI and stress response.
Keywords: Candida albicans; Cas5; Sfp1; cell wall integrity; cell wall stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cas5 Regulates the Exposure of β-Glucan, the Cell Surface Hydrophobicity, and the Expression of Cell Wall Proteins to Remodel the Candida albicans Cell Wall and Participates in the Recruitment of Neutrophils.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 19;13(3):683. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13030683. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40142575 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans Sfp1 Is Involved in the Cell Wall and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Responses Induced by Human Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10633. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910633. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638975 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Cas5 suppresses hyphal morphogenesis during yeast-form growth in Candida albicans.J Microbiol. 2021 Oct;59(10):911-919. doi: 10.1007/s12275-021-1326-y. Epub 2021 Sep 7. J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34491522
-
Fungal Cell Wall Proteins and Signaling Pathways Form a Cytoprotective Network to Combat Stresses.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Sep 8;7(9):739. doi: 10.3390/jof7090739. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the caspofungin-induced cell wall damage response in Candida albicans.Curr Genet. 2020 Dec;66(6):1059-1068. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01105-8. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32876716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resilience in Resistance: The Role of Cell Wall Integrity in Multidrug-Resistant Candida.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;11(4):271. doi: 10.3390/jof11040271. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cas5 Regulates the Exposure of β-Glucan, the Cell Surface Hydrophobicity, and the Expression of Cell Wall Proteins to Remodel the Candida albicans Cell Wall and Participates in the Recruitment of Neutrophils.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 19;13(3):683. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13030683. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40142575 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans and Candida glabrata: global priority pathogens.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Jun 27;88(2):e0002123. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00021-23. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38832801 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

