Biochemical Atypia in Russian Neisseria gonorrhoeae Clinical Isolates Belonging to the G807 NG-MAST Genogroup/ST1594 MLST
- PMID: 36422341
- PMCID: PMC9697718
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10112271
Biochemical Atypia in Russian Neisseria gonorrhoeae Clinical Isolates Belonging to the G807 NG-MAST Genogroup/ST1594 MLST
Abstract
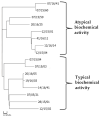
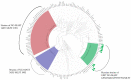
Many current gonococcal clinical isolates in Russia show atypical taxonomically significant biochemical activity, which leads to species misidentification. Molecular typing of such cultures according Neisseria gonorrhoeae multiantigen sequence typing (NG-MAST) and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) protocols assigned them to the G807 NG-MAST GENOGROUP/ST1594 MLST that has been predominant in Russia in recent years. The goal of the study was to analyze the molecular mechanisms of biochemical atypia in N. gonorrhoeae clinical isolates characterized as the members of G807 NG-MAST GENOGROUP/ST1594 MLST. Sixteen isolates of this genogroup were included in the study, eight showed defective amino acid metabolism or loss of D-glucose fermentation. Comparative bioinformatic analysis based on WGS data divided these isolates into two clusters strictly associated with typical or atypical biochemical activity. Cultures with defective amino acid metabolism had a 5-nucleotide insertion in the pip-gene that caused a stop codon and led to synthesis of the non-functional enzyme. Comparison of the sequenced genomes with publicly available N. gonorrhoeae genomes showed the rarity of this insertion. In the global N. gonorrhoeae phylogenetic tree the G807 NG-MAST GENOGROUP/ST1594 MLST forms a distinct branch characterized by 170 SNPs, most of which are non-synonymous. We hypothesized a unique strategy for G807 NG-MAST GENOGROUP/ST1594 MLST clone persistence in the global N. gonorrhoeae population via escape of antimicrobial therapy due to diagnostic misidentification.
Keywords: Neisseria gonorrhoeae; biochemical atypia; phylogenetic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative Whole-Genome Analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolates Revealed Changes in the Gonococcal Genetic Island and Specific Genes as a Link to Antimicrobial Resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 18;12:831336. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.831336. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35252037 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae multi-antigen sequence types in Russia and Europe.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Apr;93:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.020. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31978578
-
Molecular surveillance of clinical Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in Russia.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Oct;48(10):3681-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00565-10. Epub 2010 Jul 21. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20660213 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence and dissemination of three mild outbreaks of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with high-level resistance to azithromycin in Barcelona, 2016-18.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Mar 12;76(4):930-935. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa536. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33367806 Review.
-
Review and international recommendation of methods for typing neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates and their implications for improved knowledge of gonococcal epidemiology, treatment, and biology.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Jul;24(3):447-58. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00040-10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21734242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gonococcal Genetic Island in the Global Neisseria gonorrhoeae Population: A Model of Genetic Diversity and Association with Resistance to Antimicrobials.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 10;11(6):1547. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061547. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37375049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. [(accessed on 4 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/ru/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacter....
-
- Shaskolskiy B., Kravtsov D., Kandinov I., Gorshkova S., Kubanov A., Solomka V., Deryabin D., Dementieva E., Gryadunov D. Comparative Whole-Genome Analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolates Revealed Changes in the Gonococcal Genetic Island and Specific Genes as a Link to Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022;12:831336. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.831336. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

