School Refusal in Youth: A Systematic Review of Ecological Factors
- PMID: 36422762
- PMCID: PMC9686247
- DOI: 10.1007/s10578-022-01469-7
School Refusal in Youth: A Systematic Review of Ecological Factors
Abstract
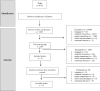
To guide school practitioners in the identification and intervention of youth with anxious school refusal, this systematic review used an ecological lens to examine the factors that differentiated children and adolescents with school refusal from those without. Based on the rigorous protocol from the Center for Reviews and Dissemination's (CRD) internationally recognized guidelines, 15 studies examining 67 different factors were identified. Results reveal 44 individual, social and contextual factors that differentiate youth with school refusal from peers without school refusal. Findings highlight the centrality of anxiety, or anxiety-related symptoms, and diverse learning needs as main points of contrast between youth with school refusal and those without. Implications of an ecological understanding of the factors associated with school refusal for selective and indicative prevention by school and mental health practitioners are discussed.
Keywords: Ecological model; School practitioners; School refusal; Systematic review.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
References
-
- Berg I. School avoidance, school phobia, and truancy. In: Lewis M, editor. Child and adolescent psychiatry: a comprehensive textbook. Sydney: Lippincott Williams et Wilkins; 2002. pp. 1260–1266.
-
- Heyne D, Landell MG, Melvin GA, Gentle-Genitty CS. Differentiation between school attendance problems: why and how? Cogn Behav Pract. 2019;26:8–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpra.2018.03.006. - DOI
-
- Havik T, Bru E, Ertesvag SK. School factors associated with school refusal-and truancy-related reasons for school non-attendance. Sch Psychol Educ. 2015;18:221–240. doi: 10.1007/s11218-015-9293-y. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources