Radiation Attenuation Assessment of Serpentinite Rocks from a Geological Perspective
- PMID: 36422904
- PMCID: PMC9698313
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10110697
Radiation Attenuation Assessment of Serpentinite Rocks from a Geological Perspective
Abstract
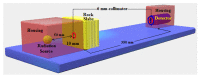
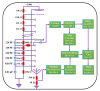
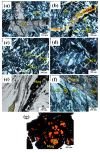
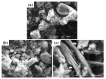
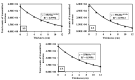
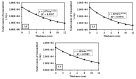
Serpentinites are metamorphic rocks that are widely applied as aggregates in the production of radiation-shielding concrete. Different varieties of massive serpentinite mountains located in Egypt exist without real investment. Hence, this study aims to evaluate the radiation shielding efficacy of three varieties of serpentinite rocks from different geological perspectives: mineralogical, geochemical, and morphological characteristics. X-ray diffraction, transmitted-light microscopy, and thermal analysis were required to characterize their mineralogical composition, while X-ray fluorescence was necessary to investigate their geochemical features. Moreover, scanning electron microscopy was used to detect their morphological characteristics. On the other hand, the PuBe source and stilbene detector were employed for the experimental determination of fast neutrons and γ-ray attenuations, which were conducted at energy ranges of 0.8−11 and 0.4−8.3 MeV, respectively. Based on the mineralogical, geochemical, and morphological characteristics of these rocks, the radiation attenuation capacity of lizardite > antigorite > chrysotile. However, these serpentinites can be applied as a natural alternative to some radiation-shielding concrete in radiotherapy centers and other counterpart facilities.
Keywords: fast neutron; geochemical and mineralogical composition; morphology; serpentinite rock; shielding; γ-ray.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

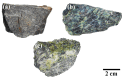

References
-
- Lee S., Kim M., Lee J. Analyzing the Impact of Nuclear Power on CO2 Emissions. Sustainability. 2017;9:1428. doi: 10.3390/su9081428. - DOI
-
- El-Samrah M.G., Tawfic A.F., Chidiac S.E. Spent nuclear fuel interim dry storage; Design requirements, most common methods, and evolution: A review. Ann. Nucl. Energy. 2021;160:108408. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2021.108408. - DOI
-
- Otto T. Safety for Particle Accelerators. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2021. Beam Hazards and Ionising Radiation; pp. 55–82. - DOI
-
- Akkurt I., Kilincarslan S., Basyigit C. The photon attenuation coefficients of barite, marble and limra. Ann. Nucl. Energy. 2004;31:577–582. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2003.07.002. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

