Physiotherapy for Cervical Dystonia: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials
- PMID: 36422957
- PMCID: PMC9694367
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14110784
Physiotherapy for Cervical Dystonia: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials
Abstract
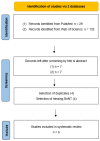
Physiotherapy is mentioned as an adjunctive treatment to improve the symptoms of cervical dystonia in terms of pain, function and quality of life. However, botulinum neurotoxin injection remains the treatment of choice. This systematic review emphasizes physical therapy and evaluates it by including six studies. The methodology is based on a previous systematic review on this topic to provide better comparability and actuality. For this purpose, two databases were searched using the previously published keywords. This time, only randomised controlled trials were evaluated to increase the power. In conclusion, additional physical therapy and active home exercise programs appear to be useful. Further research should focus on the dose-response principle to emphasize physical therapy treatment modalities.
Keywords: add-on treatment; physical therapy; rehabilitation; spasmodic torticollis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ip C.W., Bäumer T., Ceballos-Baumann A. Dystonie, S1-Leitlinie. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie. Leitlinien für Diagnostik und Therapie in der Neurologie. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie; Berlin, Germany: 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources