Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review on Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir
- PMID: 36423149
- PMCID: PMC9696049
- DOI: 10.3390/v14112540
Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review on Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir
Abstract
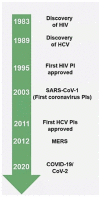
Despite the rapid development of efficient and safe vaccines against COVID-19, the need to confine the pandemic and treat infected individuals on an outpatient basis has led to the approval of oral antiviral agents. Taking into account the viral kinetic pattern of SARS-CoV-2, it is of high importance to intervene at the early stages of the disease. A protease inhibitor called nirmatrelvir coupled with ritonavir (NMV/r), which acts as a CYP3A inhibitor, delivered as an oral formulation, has shown much promise in preventing disease progression in high-risk patients with no need for supplemental oxygen administration. Real-world data seem to confirm the drug combination's efficacy and safety against all viral variants of concern in adult populations. Although, not fully clarified, viral rebound and recurrence of COVID-19 symptoms have been described following treatment; however, more data on potential resistance issues concerning the Mpro gene, which acts as the drug's therapeutic target, are needed. NMV/r has been a gamechanger in the fight against the pandemic by preventing hospitalizations and halting disease severity; therefore, more research on future development and greater awareness on its use are warranted.
Keywords: COVID-19; Paxlovid; SARS-CoV-2; nirmatrelvir; nirmatrelvir/ritonavir; ritonavir; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. [(accessed on 1 November 2022)]; Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinical-manag...
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control 2022 High-Risk Groups for COVID-19. [(accessed on 5 November 2022)]. Available online: www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/high-risk-groups.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous